Types of Redox reactions
Redox reactions are divided into two main types:
1) Inter molecular Redox Reactions: In such redox reactions, one molecule of reactant is oxidized whereas molecule of other reactant is reduced.
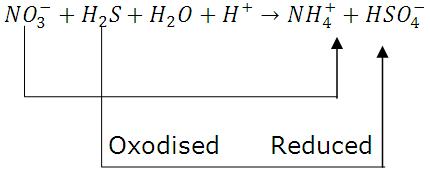
2) Intra molecular Redox Reactions: One atom of a molecule is oxidized and other atom of same molecule is reduced then it is intra molecular redox reaction.
1)Single-Replacement Redox Reactions: A + BC ®AC + B
• Conventional (Molecular) Equation
Zn(s) + Cu(NO3)2 (aq) → Zn(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s)
• Ionic Equation
Zn(s) + Cu+2(aq) + NO3- (aq) → Zn+2(aq) + NO3- (aq) + Cu(s)
• Net Ionic Equation
Zn(s) + Cu+2(aq) → Zn+2(aq) + Cu(s)
2) Combination reaction is a reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single product: A +B + C ®ABC
C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
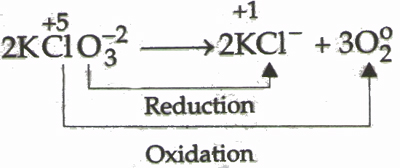
3) Decomposition reaction is a reaction in which a single compound reacts to give two or more substances, usually requiring a raise in temperature:
ABC ®A + B + C
2KClO3 (s) ® 2KCl(s) + 3O2 (g)
4) Combustion (burning) reaction is a reaction of a substance with oxygen, usually the rapid release of heat produces a flame:
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) ® CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
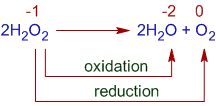
5) Disproportionation reactionis an intramolecular reaction in which the atoms of one element is reduced and simultaneously increase the degree of oxidation state.
+1 -1 +1 -2 0
H2O2 ® H2O + O2
These are reactions where a single reactant in an intermediate oxidation state reacts with itself to a higher and lower oxidation state. Here are some examples work out the balanced equations
· Cl2 in water to give HClO and Cl-
· Decomposition of H2O2 to give water andO2
· MnO2 to Mn2+ and MnO4- in aqueous acid solution
Most intermediate oxidation chlorine compounds will disproportionate as will some intermediate oxides of the transition metals and this is the main reason of instability of lower oxidation states of the group 2 and 3 metals.
Thus, the reaction that involves simultaneous oxidation and reduction of atoms of same element from one oxidation state (OS) to two different oxidation states is known as disproportionation reaction.
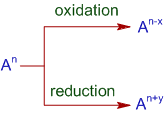
The minimum requirement for this reaction to occur is: the element undergoing disproportionation should exhibit minimum three different oxidation states.
Dissociation of hydrogen peroxide is a disproportionation reaction. The oxygen atom in H2O2 is in -1 oxidation state. It is both oxidized to O2 (ox.st = 0) and reduced to H2O (ox.st = -2).
In above reaction, the relatively less stable peroxide disproportionate into relatively more stable compounds i.e. water and dioxygen.
Disproportionation of halogens (Cl2 ,Br2 , I2) in alkali
Except fluorine, halogens (Cl2 , Br2 , I2) undergo disproportionation in alkaline medium.
They form halide and hypohalite in cold and dilute alkali.
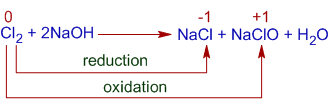
Here, one chlorine atom is oxidized to +1 and second is reduced to -1 oxidation states.
Whereas, halide and halate are formed in hot and concentrated alkali.
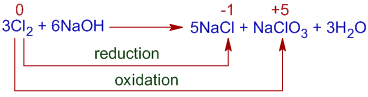
In this case, one chlorine atom loses 5 electrons and get oxidized to +5 state and five chlorine atoms are reduced to -1 state by accepting one electron each.
Disproportionation of phosphorus in alkali
Phosphorus disproportionates to phosphine and hypophosphite in alkaline medium. In this case, one P atom is reduced to -3 oxidation number (in PH3) and three P atoms get oxidized to +1 (in NaH2PO2).

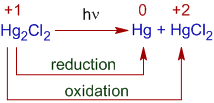
Photolysis of Mercurous chloride, Hg2Cl2
Mercurous chloride undergoes disproportionation under UV light to give mercury and mercuric chloride. The Hg22+ ion is oxidized to Hg2+ and reduced to Hg.
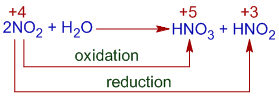
Reaction of Nitrogen dioxide with water
Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 reacts with water to give nitric and nitrous acids (Ostwald process). It is a disproportionation reaction. The Nitrogen in NO2 is in +4 oxidation state. It is reduced to nitrous acid, HNO2 in which the OS of nitrogen is +3 and oxidized to nitric acid, HNO3 in which the OS of nitrogen is +5.
An example is the disproportionation of copper in the following reaction:
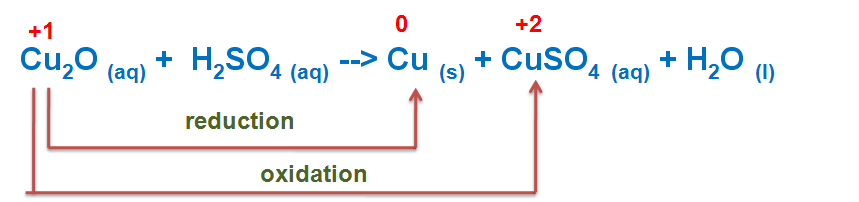
Here the copper goes from oxidation state +1 in Cu2O to oxidation state 0 in Cu and oxidation state +2 in CuSO4.
Дата добавления: 2018-11-25; просмотров: 2113;
