Special examinations. White Blood Cell Count. Acute appendicitis is not the only condition that causes elevated white blood cell counts
White Blood Cell Count. Acute appendicitis is not the only condition that causes elevated white blood cell counts. Almost any infection or inflammation can cause this count to be abnormally high. Therefore, an elevated white blood cell count alone cannot be used as a sign of appendicitis.
Urinalysis. Urinalysis is a microscopic examination of the urine that detects red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria in the urine. Urinalysis usually is abnormal when there is inflammation or stones in the kidneys or bladder. The urinalysis also may be abnormal with appendicitis because the appendix lies near the ureter and bladder. If the inflammation of appendicitis is great enough, it can spread to the ureter and bladder leading to an abnormal urinalysis. Most patients with appendicitis, however, have a normal urinalysis. Therefore, a normal urinalysis suggests appendicitis more than a urinary tract problem.
Abdominal X-ray.An abdominal X-ray may detect the faecalith that may be the cause of appendicitis. This is especially true in children.
Chest films may be performed to exclude any disease of the base of the right lung as disease in this region may irritate the spinal nerve to simulate the symptoms of appendicitis.
Ultrasonic (US). Ultrasonic can identify an enlarged appendix or an abscess. Nevertheless, during appendicitis, the appendix can be seen in only 50% of patients. Therefore, not seeing the appendix during an Ultrasonic does not exclude appendicitis. Ultrasonic also is helpful in patients with renal colic and in women because it can exclude the presence of conditions involving the ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus.
Ultrasonic target sign of acute appendicitis can be detected (fig. 5). Transverse Ultrasonic scan through an inflamed appendix shows an intact echogenic submucosal layer and a fluid-filled lumen (F), resulting in a “target” appearance.

Figure 5 – Acute appendicitis with target sign
Computerized tomography (CT) scan. In patients who are not pregnant, a CT scan of the appendix region is useful in acute appendicitis and periappendicular abscesses diagnosis (fig. 6) as well as in excluding other diseases inside the abdomen and pelvis that can mimic appendicitis.
Laparoscopy.Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure in which a small fiber-optic tube with a camera is inserted into the abdomen through a small puncture made on the abdominal wall.
Laparoscopy allows a direct view of the appendix as well as other abdominal and pelvic organs. If appendicitis is found, the inflamed appendix can be removed with the laparoscope.
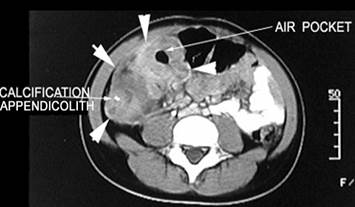
Figure 6 – Acute appendicitis with periappendicular abscesses
Дата добавления: 2015-07-04; просмотров: 1341;
