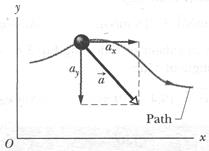
Average Acceleration and Instantaneous Acceleration
When a particle's velocity changes from 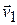 to
to 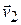 in a time interval
in a time interval 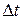 , its average acceleration
, its average acceleration 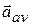 during
during 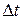 is
is
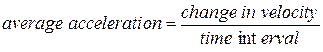
Or
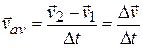
If we shrink 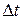 to zero about some instant, then in the limit
to zero about some instant, then in the limit 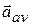 approaches the instantaneous acceleration (or acceleration)
approaches the instantaneous acceleration (or acceleration) 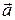 at that instant; that is,
at that instant; that is,
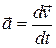 (4-16)
(4-16)
 If the velocity changes in either magnitude or direction (or both), the particle must have an acceleration.
If the velocity changes in either magnitude or direction (or both), the particle must have an acceleration.
We can write Eq. 4-16 in unit-vector form by substituting for v*from Eq. 4-11 to obtain
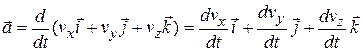
|
We can rewrite this as
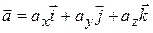 (4-17)
(4-17)
where the scalar components of 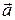 are
are
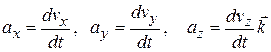 (4-18)
(4-18)
We can rewrite this as
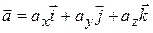 (4-17)
(4-17)
where the scalar components of 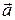 are
are
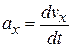 ,
, 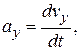
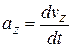 (4-18)
(4-18)
Дата добавления: 2015-06-17; просмотров: 999;
