Nursing in an endocrinology separation
Pediatric Endocrinology Nurses help kids with endocrine diseases. These nurses treat infants to teens with delayed growth and development, and diseases like diabetes, hypoglycemia, and endocrine gland disorders including adrenal, thyroid and pituitary problems. As a Pediatric Endocrinology Nurse, you'll work closely with pediatricians to help develop your patients' treatment plan and care. Since one of the most common diseases in pediatric endocrinology is juvenile diabetes, you'll play an important role in teaching children and their parents about the effects of diabetes, and help them make healthy lifestyle choices.

Things You'll Do:
· Conduct tests to monitor patient progress
· Anticipate new health problems
· Take blood pressure and draw blood samples
· Help patients, and their parents, manage their diseases
· Teach families about healthy lifestyle choices
Your job characteristics:
· Multifaceted
· Structured
· Patient-facing
· Research-oriented
Method for the care of children suffering from diabetes. A patient with all of its problems is the focus of nurses and doctors. Many children find themselves for the first time in the hospital, and one of the tasks of nurses - to help the child to adapt to the conditions of the hospital. Nurse psychological support both children and parents is a negative-minded approach to the children around them with care and warmth. Application of the nursing process requires the nurse not only expertise, but also the skills of communication, as well as a creative approach to the performance of their official duties. All nurses regularly improve their professionalism in seminars conducted in the department. Nursing process includes the following steps: survey, identify the problem, develop a plan of action and the nurse doing it and, finally, evaluate the effectiveness of their actions. All actions of the nurse closely linked and follow one from the other.
Work nurse in the endocrinology department Must record all patient complaints, of which the most characteristic are: sweating, tachycardia, changes in body weight, change in shape of the neck, irritability, thirst, itching, polyuria, weakness. In an interview with the patient to find a family history of endocrine diseases, especially food of the patient, past illnesses, occupation, working and living conditions, the presence of trauma, addictions and stress. Examining the patient should pay attention to the "eye symptoms,' enlargement of the thyroid gland, depletion, obesity, pigmentation of the skin, hand tremor, the condition of hair and nails, the presence of boils. In a conversation with patients suffering from thyrotoxic goiter, you need to pay attention to the specific complaints: increased excitability, irritability, sweating, sleep disturbance. Need to find out what factors contributed to the development of the disease. On examination, patients with endocrine nurse should pay attention to the triad of symptoms: swelling of the thyroid gland, exophthalmos, tachycardia. Patients with hyperthyroidism usually have expressed disorders of the nervous system and the psycho-emotional sphere, so the part of the nurse requires patience, attention and sensitivity to such patients. When working with patients with diabetes should pay attention to the initial symptoms of the disease: increased thirst, increased urination, dry skin, itching. On examination, patients pay attention to the condition of the skin: scratches, pustular disease. Patients with long- term diabetes mellitus are predisposed to the following complications: neuropathy, angiopathy, gangrene of the extremities, coma, retinopathy, kidney disease, neuralgia. Tc get a complete picture of the disease, the nurse should know the results of additional methods of examination. Based on these data the nurse develops a plan of care for patients. The nurse explains to patients with diabetes mellitus of adhering to diet, principles of prevention comatose states, introduces measures which the patient himself can take. Blood tests carried out strictly in sugar on an empty stomach, as warn the patient. In the appointment of a patient "sugar curve," the nurse warned the patient about the time of blood sampling, as well as on minimal exertion on the day of the study. Urine for sugar patient collects during the day in a large container. Before you go to the lab nurse mixes urine and molds 150-200 ml. A nurse must be able to promptly assess the condition of the patient on the basis of his complaint. Timely recognition prekomatoznoe and comatose states can correctly and quickly provide the necessary assistance. Caring for patients with diabetes, the nurse must remember that negative emotions can lead to decompensation of diabetes. The nurse teaches the patient methods of use insulin syringe and self-administration of insulin. The nurse must monitor compliance with the sick diet, so as of eating disorders can lead to the breakdown of compensation of diabetes. Nutrition of patients must be complete, with only a restriction of carbohydrates. Food must contain sufficient amounts of vitamins, it is necessary to accept small portions: 5-7 times a day. Food patients with thyrotoxicosis should be varied, rich in vitamins. Should limit consumption of meat, fish, drinks, stimulating the nervous system. The nurse should monitor adherence, personal hygiene, the condition of the respiratory and cardiovascular system (counting the number of breaths, the definition of pulse, blood pressure).Kussmaul's coma Factors contributing to the development of diabetic coma are: violation of the treatment, nutrition, trauma, infections, intoxication. In prekomatoznoe condition the patient has the feeling of thirst, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, headache. Symptoms: the smell of acetone breath, tachycardia, dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, "noisy breathing", lowering blood pressure, hypotension, eyeballs and muscles, hyperglycemia, glycosuria. Actions nurse: seek medical advice immediately, insulin intravenously, detoxification therapy.Hypoglycemic coma Factors contributing to the development of hypoglycemic coma are of eating disorders, an overdose of insulin, physical overload. In the pre-comatose patient has weakness, sweating, pale skin, muscle stiffness, restlessness, tremor of the body, muscle stiffness. Symptoms: increased sweating, dilated pupils, bradycardia, decreased blood pressure, hypoglycemia, seizures. Actions nurse: call the doctor to give the patient a few lumps of sugar, glucose intravenously, epinephrine, prednisolone (hydrocortisone).
Nose
Your nose is important to your health. It filters the air you breathe, removing dust, germs, and irritants. It warms and moistens the air to keep your lungs and tubes that lead to them from drying out. Your nose also contains the nerve cells that help your sense of smell. When there is a problem with your nose, your whole body can suffer. For example, the stuffy nose of the common cold can make it hard for you to breathe, sleep, or get comfortable.
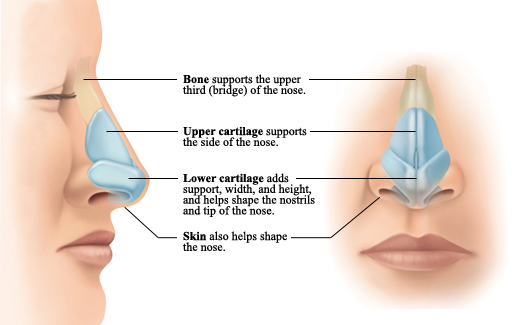
Many problems besides the common cold can affect the nose. They include Deviated septum - a shifting of the wall that divides the nasal cavity into halves Nasal polyps - soft growths that develop on the lining of your nose or sinuses Nosebleeds
Rhinitis - inflammation of the nose and sinuses sometimes caused by allergies. The main symptom is a runny nose.
Nasal fractures, also known as a broken nose.
 Throat
Throat
Your throat is a tube that carries food to your esophagus and air to your windpipe and larynx. The technical name for throat is pharynx.
Throat problems are common. You've probably had a sore throat. The cause is usually a viral infection, but other causes include allergies, infection with strep bacteria or the upward movement of stomach acids into the esophagus, called gastric reflux.
Other problems that affect the throat include
Tonsillitis - an infection in the tonsils
Pharyngitis - inflammation of the pharynx
Most throat problems are minor and go away on their own. Treatments, when needed, depend on the problem.
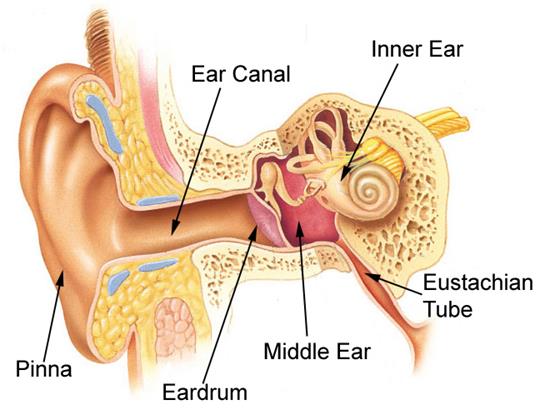
Ear
Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them in hearing. Sound waves come in through your outer ear. They reach your middle ear, where they make your eardrum vibrate. The vibrations are transmitted through three tiny bones, called ossicles, in your middle ear. The vibrations travel to your inner ear, a snail-shaped organ. The inner ear makes the nerve impulses that are sent to the brain. Your brain recognizes them as sounds. The inner ear also controls balance.
A variety of conditions may affect your hearing or balance:
Ear infections are the most common illness in infants and young children.
Tinnitus, a roaring in your ears, can be the result of loud noises, medicines or a variety of other causes.
Meniere's disease may be the result of fluid problems in your inner ear; its symptoms include tinnitus and dizziness.
Ear barotrauma is an injury to your ear because of changes in barometric (air) or water pressure. Some ear disorders can result in hearing disorders and deafness.
Дата добавления: 2015-06-10; просмотров: 1449;
