Cybernetic methods of Data Mining
The second direction of Data Mining - is a variety of approaches, united by the idea of computer mathematics and the use of artificial intelligence theory.
This group includes such methods:
• Artificial neural networks (pattern recognition, clustering, forecasting)
• evolutionary programming (including algorithms method of group account of arguments)
• genetic algorithms (optimization)
• associative memory (search analogues, prototypes)
fuzzy logic;
• decision trees;
• expert knowledge processing systems.
Data Mining techniques can also be classified according to Data Mining tasks.
In accordance with this classification select two groups. The first of them - a division of Data Mining techniques to solving the problem of segmentation (ie the problem of classification and clustering) and forecasting tasks.
According to a second classification by the tasks Data Mining techniques can be directed to the descriptive and predictive results.
Descriptive methods are used to find templates or models that describe the data that lend themselves to interpretation in terms of the analyst.
Methods aimed at obtaining descriptive results are iterative cluster analysis methods, including: k-means algorithm, k-median, hierarchical cluster analysis methods, Kohonen self-organizing maps, methods of cross-tabular visualization, various imaging techniques and others.
Predictive methods use the meaning of some variables for predicting / forecasting unknown (missing) or future values of other (target) variables.
Methods aimed at obtaining predictive results include methods such as neural networks, decision trees, linear regression, nearest neighbor, support vector machines, and others.
Data Mining Tasks
Tasks Data Mining are sometimes called regularity and techniques
There is no unified opinion as which tasks should be assigned to Data Mining. Most reputable sources list the following: classification, clustering, forecasting, association, visualization, analysis, and detection of abnormalities, evaluation, analysis of the relationships, summarizing.
Data Visualization - is the provision of information with help of pictures, graphs, charts, tables and diagrams. Value visualization is that it often allows the most clearly and concisely identify and display information contained in the data, because the image can immediately show that will take more than one paragraph in the verbal equivalent.
The development of methods of visual presentation of the data are equally attended by IT professionals and designers, as the design depends largely on how clear and "read" is visualization.
With the help of data visualization solve the most different problems.
At first, it is an important tool in the initial stages of the data analysis. The most simple of graphics allow you to quickly find data regularities, trends or anomalies, which will be guided by the analyst in the further work with the data. Similarly, the journalist, using charts when viewing the primary data, may formulate questions for themselves, from which further can lead story for another material.
Second, visualization often play an important role in the presentation of the final results of analysis. This can be static graphs showing trends; interactive visualization, allowing users to explore the data; and infographics (static and interactive), clear image is based on data history.
Important task of visualization is that in a single image with a limited number of physical measurements (typically two-dimensional) display data contained in the plurality of measurements and the relationship between them.
Questions
1.How to determine the Pearson correlation coefficient?
2. How to solve Data Mining Tasks?
3. What does processing large amounts of data mean?
4. What types have a decision tree?
References
1. June J. Parsons and Dan Oja, New Perspectives on Computer Concepts 16th Edition - Comprehensive, Thomson Course Technology, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc Cambridge, MA, COPYRIGHT © 2014.
2. Lorenzo Cantoni (University of Lugano, Switzerland) James A. Danowski (University of Illinois at Chicago, IL, USA) Communication and Technology, 576 pages.
3. Craig Van Slyke Information Communication Technologies: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications (6 Volumes). ISBN13: 9781599049496, 2008, Pages: 4288
4. Utelbaeva A.K.,Utelbaeva A.K. Study guide for lectures on discipline “Computer science”, Shimkent 2008, 84 pages.
Lecture №7. Networks and telecommunications.
Purpose: to develop a solid grasp of network by introducing the basic concepts.
Plan:
1.End devices, data transfer devices, transmission medium. Types of networks. 2.Stack protocols: TCP/IP, OSI. IP addressing. Local and wide area networks.Wire and wireless network technologies.
3. DHCP protocol. Technologies of connection to the Internet.
4.Telecommunication technologies.
1.End devices, data transfer devices, transmission medium. Types of networks.
What is a Computer Network?Two or more independent computers connected together through a communication media form a computer network. The computers are connected in a network to exchange information and data. The computers connected in a network can also use resources of other computers such as software packages and peripherals like modems, printers, backup drives, or CD-ROM drives. Networks are built with a mix of computer hardware and computer software. Further, you do not need the same software package installed on your machine, if your network has that software installed on one of the machines on the network. In this sense, computer networks are clear means for sharing resources. This makes the use of computer technology cost effective. Following Figure 8 shows a typical network with four computers.
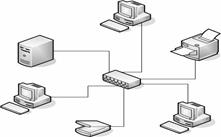
Figure 6- Typical computer network
Дата добавления: 2017-05-18; просмотров: 2476;
