The intersection of gravity sewer pipe networks with obstacles
During laying sewer systems encountered obstacles and cut s and O type: rivers, ravines, sofa, underground pipelines and facilities, and roads. Method of section depends on the position of sewage plumbings and type of barriers, as well as local conditions.
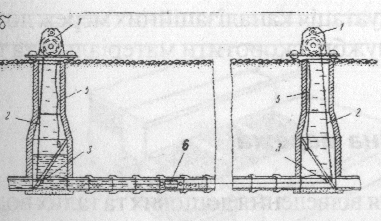
If sewage pipes located significantly higher than barrier, section executed as self-ffloating pipeline, which lies on estacade. Estacade – is supporting construction in shape of bridge (dr.2.13). Pipeline lies in isolate place without inclination change, which is given to collector. Estacades are made from combinedreinforced concrete on reinforced concrete and metal supports.
If sewage plumbings located significanty lower than barrier, crossection is executed ina view of self-floating plumbing, located in case or passing or non-passing tunnels (dr. 2.14)
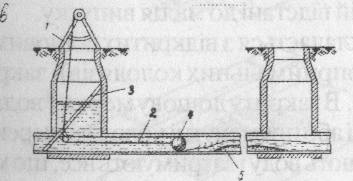
If sewage plumbing and barrier located at the same mark or their differenceis not significant, crossection is executed in a view of duker – pressure plumbing, which connects two self-floating plumbings (dr. 2.15). All plumbings dukers have top and bottom cameras and executed not less than in two thread, each of which is working.
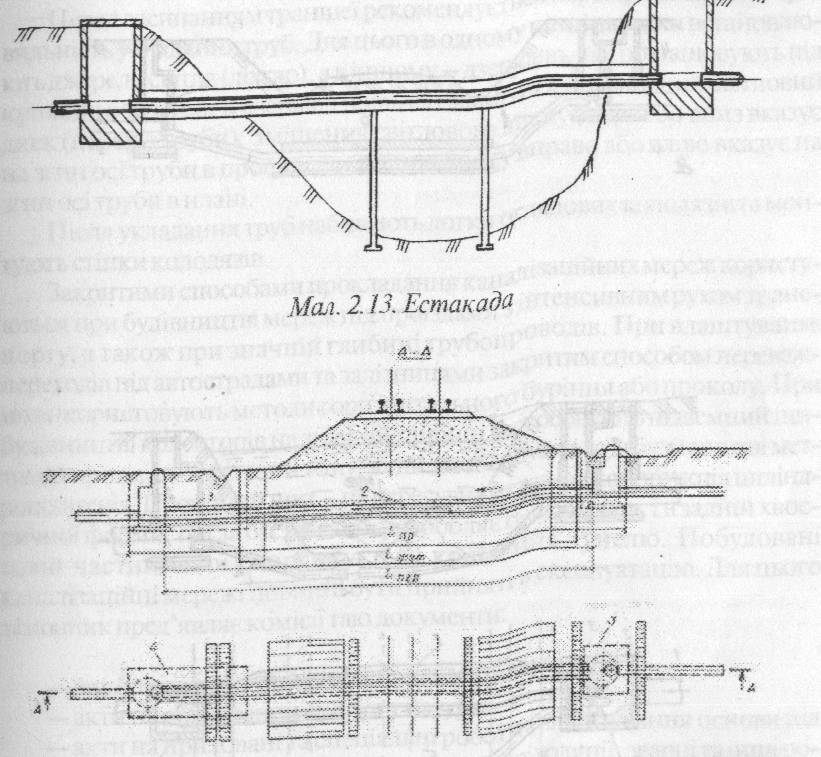
Fig. 2.14. Crossing the railway gravity pipeline:
I - Case, 2-pipe
2.2.9. Construction and operation of sewer networks
Sewage networks are built on the agreed and approved by projecting-estimate documentation in accordance with whipping network in kind. Technical supervision of construction by the customer (the department of capital construction and technical supervision service) and project organization.
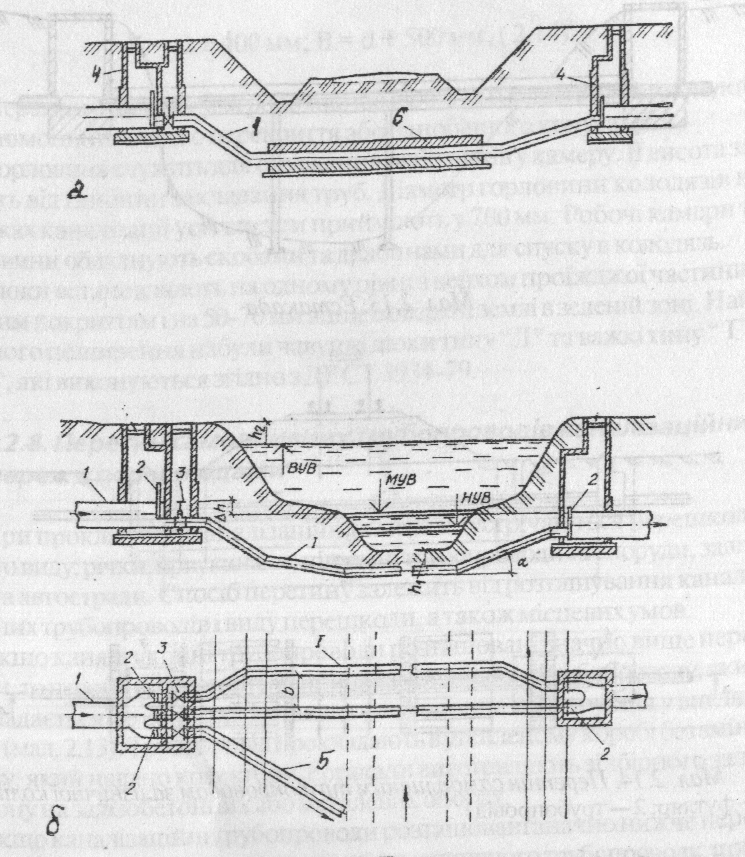
Drawing 2.15. Dukers:
a- Under transport roads; b – under water barrier; 1 – plumbing; 2 – shiber; 3 – bolt; 4 – well; 5 – emergency escape; 6 – case.
Constructing of sewer networks spend mostly open (trenchless) method. Trench at the same time arranged with the slopes or vertical walls nymy. In the latter case, there performing dill trench walls. The nature of attachment depends on the depth of transche, soil properties, the availability of groundwater. The depth of open trench shall not exceed 5 - 6 m in saturated soils and 7 - 8 m in dry soils.
Pipes are beginning to put on the bottom of the well mouth upstream water. Simultaneously with the construction of pipe sealing joints.
Before backfilling the trench is recommended to check the light right laying pipes. For him, at one end section established light source (lamp), and in another mirror, which is placed at an angle to the axis of the tube. In the mirror to impress correct * and luminous disk (pipe section). Light shift drive up or down indicates the fold axis of the tube in the profile; offset disk left or right indicates the fold axis of the tube in the plan.
After laying of pipes stuffed with trays of manholes and install walls of wells.
Closed means laying sewer used at building networks under heavy traffic passing from the transport, and also at a considerable depth of pipelines. When the device transitions under roads and railways closed overwhelming but using horizontal drilling techniques or puncture. During the construction of reservoirs at great depths underground use shield passage, similar to that used in the construction of undergrounds. Passing shield is a mobile metal construction of cylinder design, under protection of which nature is elaborated, and in the end part of which onstructed strengthening of the tunnel. Constructed sewer network must be taken into operation. For this customer makes such commission of documents:
- Run-built drawings on the network;
- Acts of slaughter facilities in kind;
- Acts on hidden and special work (placement basis under the pipe, sealing joints, waterproofing, welded, and other works);
-Approval of all project changes (with the customer and the authors development);
-Acts on the hydraulic test (for eksfiltratsiyu and infiltration);
-Passport to the pipe, building materials and details;
-Reference from exploitating organization about terms of liquidation of defects, if they were.
When taking into operation of sewer networks, particularly attention should be paid to:
a) quality basis under pipes and sealing joints along the length of the junction "(recorded in the acts of hidden work);
b) checking straightness laid mizhdvoma compatible range wells tubes to light. On examination of the pipeline is allowed deviation of the image the correct range for no more than 1 / 4 diameter horizontally, but not more than 50 mm in each direction. Deviations from the right going in the right form vertically is not permitted;
c) hydraulic testing of pipelines. Pipelines for emission-vuyutsya for leakage of water from them by the number of top up the tank water (Fig. 2.16), as well as visually on infiltration (ingress of ground water in the pipes and wells at a high level of groundwater) in the presence potoku'vody the pipe. Results of hydraulic trials comparing with dta of the table. 2.4.
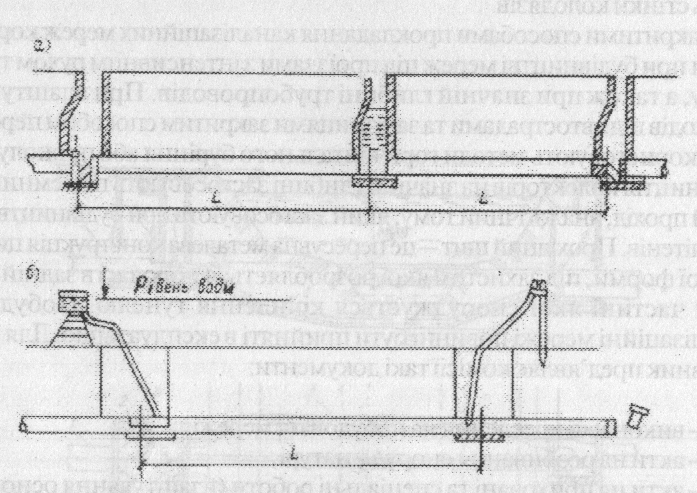
Fig. 2.16. Scheme of hydraulic test of sewage plumbings: a - after installation of wells, and b – before installation of wells
For normal operation of the sewerage network to its secu rebiynoyi work should be carried out supervision of the technical condition of etwork. The external review of the network that carried out by one or two workers,defined defects of hatches and neck of the wells, soil sitting on the highway and near the wells. The frequency of such reviews' - once every two months.
Technical inspection of sewer networks and carried out - • 2 times a year team of three mechanics. The purpose of inspection, damage detection network (state covers, trays, staples), presence of infiltration and ventilation, the degree of filling pipes need cleaning and maintenance.
Table 2.4
Allowable values of affluents or water losses through joints and walls of plumbings.
| Conditional diameter of plumbing, d, mm | Allowwable volume of affluent for 10 m length per 30 minutes for tubes | ||
| concrete | ceramic | Asbestos-cement | |
| 1,0 | 1,0 | 0,3 | |
| 4,2 | 2,4 | 1,4 | |
| 5,4 | 3,6 | 1,8 | |
| 6,7 | 4,2 | 2,2 | |
| 7,5 | 4,6 | - | |
| 8,3 | 5,0 | - |
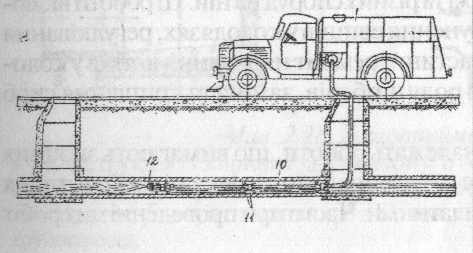
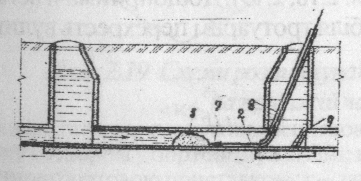
Drawing 2.17. Schemes of network cleaning: a – hydraulic; b,c,d – mechanical; 1 – winch; 2- rope; 3 – support rail; 4 – ball; 5 – jam; 6 – cylinder; 7 – tip; 8 – tube; 9 – net; 10 – hose; 11 – muff; 12 – nozzle.
Cleaning of the network in exploitation period divided into two types: profilactical and emergency. It memay realized by hydraulic or mechanical methods(dr.2.17)
Hydraulic cleaning consists in watering and gab of sediments by water stream, that is given under pressure immediately in pipe from special car. Such a cleaning realized with full mechanization of works and is quite progressive from sanitary point of view. In hydraulic way cleaned everyday, rain, production and common given networks with diameter from 150 to 600 mm.
Hydraulic cleaning and transport based on dilution and transporting flow-ability 'waste or imported water. The flow of water with higher speed, formed in any way, blurs and transports sediment downstream. For hydraulic cleaning used floating tool in the form of cylinders or balls.
When mechanical cleaning using special bar , rope or wire, and use the winch for special devices (ruffs, Buckets, etc.).
Re montni work performed during the operation kanalizadiynyh networks are divided into two types, current and capital repairs.
To maintenance belong all kinds of work, causing seasons target country and the normal operation of the network of them buildings on it. And II work included suede covers shocks eliminate fistulas in wells at the level of regulation covers the roadway, repair of packing trays in a circle, repair valves, various damper, replacement and mounting clips and more.
• To overhaul includes work requiring considerable effort and materials, namely the establishment of new and replacement of old wells and pipes, which have become unfit. Often during these works on the network disconnected.
Well-organized operation sewer "networks allowed exigencies considerably extend their service life, reduce material and pipeline trust expenses.
Дата добавления: 2015-09-07; просмотров: 1462;
