Rainy sewer network
Rain sewage used for diverting rain and tatah waters. It usually trasuyut the shortest distances to the place of issue.
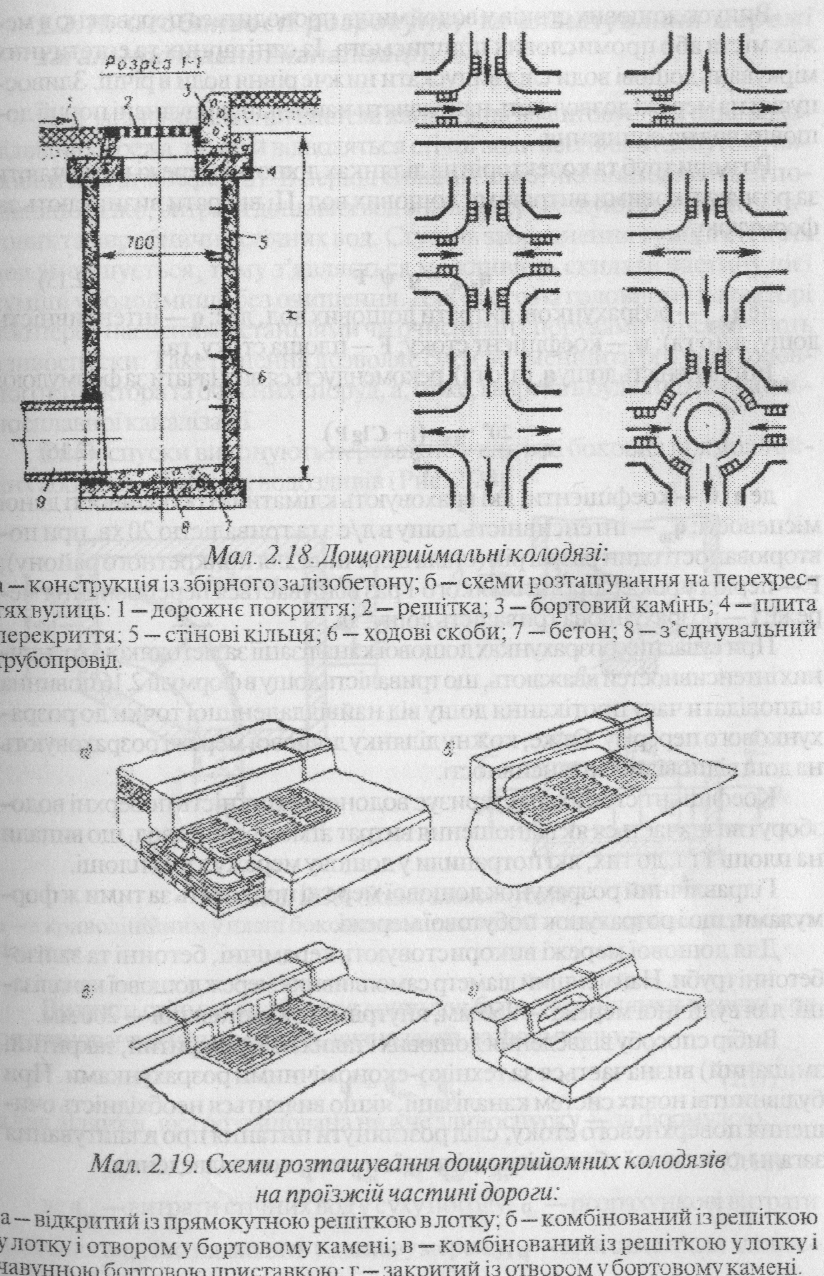
External rainwater drainage consists of open rain trays, outlets (doscholryymalnyh wells), a closed network of pipes, water-pour-off and issues. In a closed network of rain water in through outlets-complexes are round or rectangular pits covered with metal grates that let water and delay anything that can clog the sewer network (Fig. 2.18,2.19). Storm-water inlets estab most oil in a lower part of the passages near the sidewalks and intersections of streets at a distance of 50 - 80m apart.
 Issue rainwater in reservoirs is conducted mainly in the borders city or industrial enterprises. From the sanitary and aesthetic thinking water should produce below the water level in the river. Pour-off on the network can send the most contaminated portions of rain waters for cleaning.
Issue rainwater in reservoirs is conducted mainly in the borders city or industrial enterprises. From the sanitary and aesthetic thinking water should produce below the water level in the river. Pour-off on the network can send the most contaminated portions of rain waters for cleaning.
Sizes of pipes and sewers in areas of rain chains determine settlement costs for rainwater. These ones. flow determined by the formula (2.15):
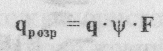
where chrshr and settlement costs rainwater, l / s, I-intensity rain, l / (g ha); \ | /-runoff coefficient, R-square sink, ha.
Ietensity of rain, q (l / SGA), it is recommended to determine the formula (2.16):
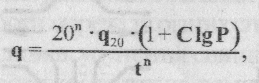
Where n and C - coefficients that take into account the climatic features of the area, q - intensity of rain in l / s per hectare Stu 20 minutes long once a year (a constant for a particular area), P - period in years, during which time an overflow occurs of network, and - estimated duration, min.
In modern calculations of rain water by methodics of boundary intensities them believe that duration of rain in formula 2.16 should correspond to the time course of rain from farthest point to the calculated section. So each rain area networks rely on the rain of the intensity.
Run-off coefficient characterizes waterproof surface water collection and is defined as the cost of atmospheric water, which issued on area 1 ha, to those who have fallen in the rain with this network space.
Hydraulic rain network calculation carried out by the same form mules as the calculation of home network.
For rain network using ceramic, concrete and ferro-concrete pipes. The smallest di ametr gravity networks of rain sewage: for the street network, 250 mm, in-block-200 mm.
Choice of diversion of rain and melt water (open, closed, mixed) is determined by technical and economic calculations. During the construction of new sewage systems, if need be clearing air governmental runoff, should overlook issue about placing of total-flow or semidivided drainage system.
2.2.11. Features calculation and installation of network zahalnosplavno / 'sewage
Whentotal-flow sewerage system is arranged a water exhaust network on which the discharged waste water of all kinds (household, industrial and atmospheric). During heavy rains, which are repeated in rarely cost rainwater exceed costs of everyday and industrial wastewater. The degree of contamination of the mixture of waste water is reduced, so it is possible to reset the part 'of this mixture in the reservoir without purification. For this purpose, the main collector or before pumping stations or treatment facilities provide rain-off. The decision to significantly reduce head collector and treatment facilities, and, consequently, the cost of construction total-flow sewage.
Rain-off serving mostly as a side-straight-linear them or curvilinear Drains (Fig, 2.20).
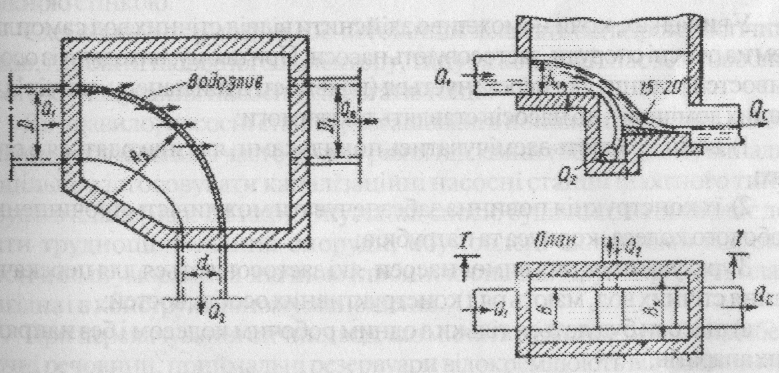
Drawing. 2.20. Plans of rain-off: a - curved-in terms of side-weir, b-with pop-up and overflow threshold.
Loss of sewage in the rain for any area network that is located to rain-off, determined by the formula(2.17):
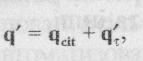
and for areas located below rain-off - by the formula (2.18):
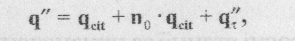
where q – expenses of sewage water dry weather; h - estimated costs of rainwater matched coming into the network before and catching; h "- the same after-rain—off to calculation part; nq- losses of rain waters, which passedrain-off, n – coefficient of dilution (taken in limits 0,5 – 5 dependingly on hydraulic characteristics of water f low and location of rain-off).
Diameters of pipes of total-flow network taken in calculation of full filling of pipe at acalculational losses of all types of drain waters during rain. Hydraulic calculation of total-flow network is checked on capacity only industrial and everyday waters. In that case velocities of flow should be not less than minimal, i.e. should be provided self-cleaning of the network in dry weather.
Дата добавления: 2015-09-07; просмотров: 936;
