Theoretical part. Fundamental characteristics of the electron are charge and mass
Fundamental characteristics of the electron are charge and mass. Relation of the charge of the electron to its mass is a specific charge of the electron:
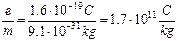
 This characteristic of the electron we can obtain by a magnetron method. This method makes use of the influence of a magnetic field on the electron that moves in a radial electric field. The electron tube is in the magnetic field of a solenoid. The electric field is perpendicular to the magnetic one. The electrons in the electron tube move from the cathode to the anode along a radius (1) if the magnetic field is absent (Fig.15.1).
This characteristic of the electron we can obtain by a magnetron method. This method makes use of the influence of a magnetic field on the electron that moves in a radial electric field. The electron tube is in the magnetic field of a solenoid. The electric field is perpendicular to the magnetic one. The electrons in the electron tube move from the cathode to the anode along a radius (1) if the magnetic field is absent (Fig.15.1).
Lorenz’s force acting on the electrons when they move in the magnetic field of the solenoid is 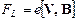 , and therefore trajectory of motion will be distorted (curve 2 in the Fig.15.1).
, and therefore trajectory of motion will be distorted (curve 2 in the Fig.15.1).
The trajectory of the electron will be closed when intensity of the
Figure 15.1 magnetic field is quit sufficiently high. In this case the specific charge of the electron is defined as:
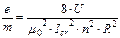 , (15.1)
, (15.1)
where U - potential difference of the cathode and anode; m0 - magnetic constant; Icr - critical current of the solenoid; n - quantity of turns per unit of the solenoid length; R - radius of solenoid.
Дата добавления: 2015-03-20; просмотров: 756;
