Dependence of Rates on Concentration
CHEMICAL KINETICS
Chemical Kinetics
Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur.
Four important factors affect rates of reactions:
1.reactantconcentration
Temperature
Catalyst
4.surfacearea
Reaction Rates
Speed of a reaction is measured by the change in concentration with time.
Suppose A reacts to form B.
For the reaction A B there are two ways of measuring rate:
1. the speed at which the products appear (i.e. change in concentration of B per unit time), or
2. the speed at which the reactants disappear (i.e. the change in concentration of A per unit time).
Average rate = change in concentration of B or A = D[B] = -D[A]
time required for this change D t D t
Unit of average rate is mol/L*s or [M/s].
The rate at any instant (instantaneous rate) is the slope of the tangent to the curve (r =-d[A]/dt) Instantaneous rate is different from average rate.
We usually call the instantaneous rate the rate.
Reaction Rates and Stoichiometry
In general for
aA + bB cC + dD
rate = - 1d[A] = - 1d[B] = 1d[C] = 1d[D]
a dt b d t c d t d d t
Dependence of Rates on Concentration
In general, rates increase as concentrations increase.
For the reaction:
NH4+(aq) + NO2-(aq) N2(g) + 2H2O(l)
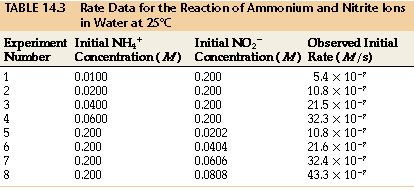
We note:
- as [NH4+] doubles with [NO2-] constant, the rate doubles,
- as [NO2-] doubles with [NH4+] constant, the rate doubles.
We conclude rate a [NH4+] [NO2-]
Rate law:
Rate = k*[NH4+]*[NO2-]
The constant k is therate constant
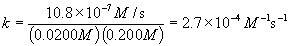
Note that the rate constant k does not depend on concentration.
For a general reaction with rate law:
Rate = k*[reactant 1]m*[reactant 2]n
We say the reaction is m-th order in reactant 1 and n-th order in reactant 2.
The overall order of reaction is m+n.
A reaction can be zeroth order if m, n are equal to zero.
· Note the values of the exponents (orders) have to be determined experimentally. They are not simply related to stoichiometry.
Дата добавления: 2018-11-25; просмотров: 400;
