Temperature and Rate
· Most reactions speed up as temperature increases. (E.g., food spoils when not refrigerated.)
· As temperature increases, the rate increases.
· Since the rate law has no temperature term in it, the rate constant must depend on temperature.
The Collision Model
· Goal: develop a model, which explains why rates of reactions increases as concentration and temperature increase.
The collision model: in order for molecules to react they must come into direct contact via collision and must possess a minimum kinetic energy to react
· The greater the number of collisions the faster the rate.
· Complication: not all collisions lead to products. In fact, only a small fraction of collisions leads to product.
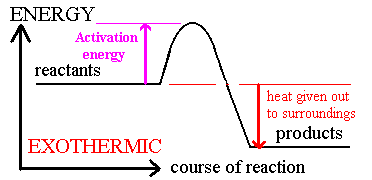
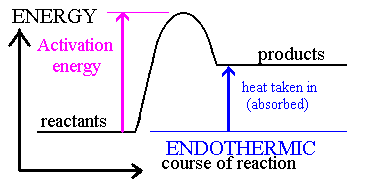
Activation Energy
Arrhenius: molecules must possess a minimum amount of energy to react.

Activation energy, Ea, is the minimum energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
· In order to form products, bonds must be broken in the reactants.
Bond breakage requires energy
Example:
Consider the rearrangement reaction of the conversion of methyl isonitrile CH3NC to methyl acetonitrile CH3CN.
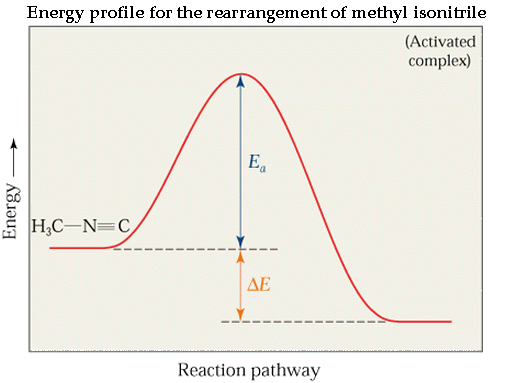
· As the temperature increases, the bond bends until the C-N bond breaks and the NC portion is perpendicular to the H3C portion.

· This structure is called the activated complex or transition state.
The energy required for the above twist and break is the activation energy, Ea.
Once the C-N bond is broken, the NC portion can continue to rotate forming a C-C N bond.
· The change in energy for the reaction is the difference in energy between CH3N C and CH3C N.
· The activation energy is the difference in energy between reactants, CH3NC and transition state.
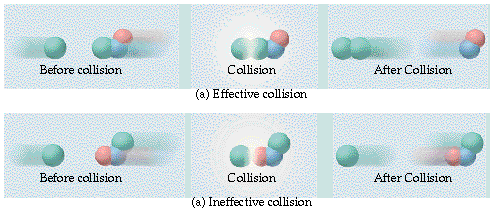
In order for reaction to occur, the reactant molecules must collide with enough energy in the correct orientation to form products.
· Consider the reaction between Cl and NOCl:
If the Cl collides with the Cl of NOCl then the products are Cl2 and NO.
If the Cl collided with the O of NOCl then no products are formed.
· We can qualitatively explain the various influence of concentration and temperature on the rate of reactions based on collision model:
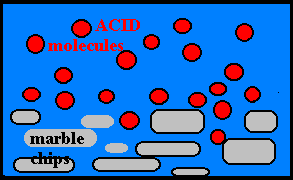
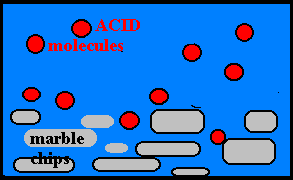
Effect of Concentration:
· The more molecules present, the greater the probability of collisions and the faster the rate.
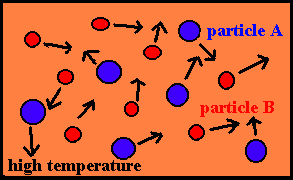
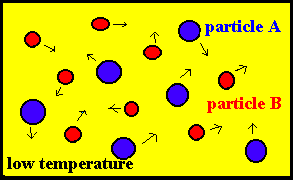
Effect of Temperature
· The higher the temperature, the more energy available to the molecules and the faster the rate.
Дата добавления: 2018-11-25; просмотров: 371;
