Experiment 8. Qualitative reaction to vitamin РР (nicotinamide, nicotinic acid).
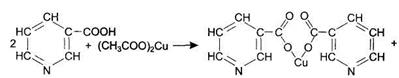
Dissolve 5-10 mg of nicotinic acid in 10-20 drops of 10% acetic acid solution and heat. Add the equal volume of 5% copper acetate solution to the solution heated up to boiling. The liquid becomes blue, and when left to stand undisturbed, the blue colored sediment of copper salt of nicotinic acid settles down.
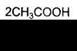
Experiment 9. Qualitative reaction to vitamin С (ascorbic acid).
9.1. Interaction of vitamin С with К3[Fe(CN)6].Add some drops of 5% potassium hydroxide solution and 10% К3[Fe(CN)6] solution to 5 ml of 0,02% vitamin C solution and mix, then add 2-3 drops of 10% hydrochloric acid solution and 1-2 drops of 10%iron chloride (III) solution. You will see blue-green coloring and gradually settling down blue sediment of Berlin blue (ferric ferrocyanide) - Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3.
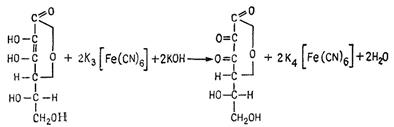
L- ascorbic acid L- dehydroascorbic acid
3K4[Fe(CN)6] + 4FeCl3 → Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 ↓ + 12KCl
Reaction with methylene-blue.
Pour 2 drops of 10% methylene-blue solution, 2 drops of 10% sodium hydrocarbonate solution, 10 drops of vitamin C solution into a test tube and heat. The liquid becomes transparent.
Test questions
1. What substanses belong to vitamins? What is their general function in an organism?
2. List the biochemical functions of the vitamins which were identified in the laboratory work.
3. Define the terms: avitaminosis, hypovitaminosis and hypervitaminosis.
Дата добавления: 2018-09-24; просмотров: 717;
