Experiment 4. Qualitative reaction to vitamin K (vicasol).
Add 5 drops of aniline to 0,5 ml of 0,2% vicasol solution in ethanol and mix. The mixture will get red coloring.
Experiment 5. Reaction of vitamin В1 (thiamine) oxidation into thiochrome.
Pour 5-6 drops of 5% К3[Fe(CN)6] solution and 1 ml of 30% sodium hydroxide to 0,5 ml of thiamine solution and mix. Then add 1 ml of isobutyl alcohol and shake intensively during 1-2 minutes. You can observe blue fluorescence in UV rays in the upper spirit layer. Heat the mixture in the test tube in a water bath, stirring. You will observe yellow coloring appearance. The fluorescence and the yellow coloring are caused by thiochrome formation:
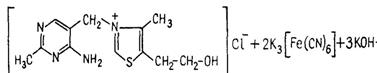 ®
®
Thiamine chloride
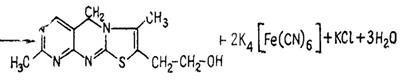
Thiochrome
Experiment 6. Qualitative reaction to vitamin В2 (riboflavin).
Pour 10 drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid and add a piece of zinc metal to 0,5ml of riboflavin solution. Hydrogen bubbling is beginning and the liquid is gradually getting pink and then it is decolorizing. The reaction is caused by riboflavin reduction first into rhodoflavin of red coloring and then into colorless leucoflavin. When the bleached solution is shaken, the leuco compound is again oxidized by aerial oxygen into riboflavin:
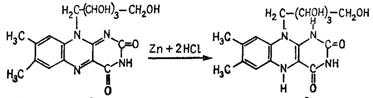
Riboflavin Leucoflavin
Experiment 7. Reaction of vitamin В6 (pyridoxine) with iron chloride (III).
Pyridoxine is a general definition for a group of chemical compounds that possess the activity of vitamin В6:
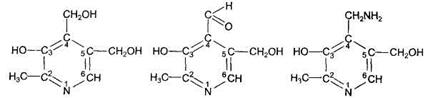
Pyridoxol (pyridoxine) pyridoxal pyridoxamine
Pour 5-10 drops of 5% vitamin В6 water solution into a test tube, add 1-2 drops of 5% iron chloride solution. After shaking the mixture there will be a red-colored liquid. A complex compound of iron phenolate type is formed.
Дата добавления: 2018-09-24; просмотров: 772;
