Inhibitory effect of chloride ions on dehydrogenase complex of potatoes.
Potatoes cut into slices. One slice left to control, the second is sprinkled with sodium chloride, the third - potassium iodide, the fourth - potassium chlorate. After 15 - 20 minutes three slices become dark, and sprinkled with sodium chloride mains unchanged.
2. Identifying the activity of α-amylase according to Wolgemut.
The method is based on identifying the ultimate dissolving of α–amylase solution which still allows splitting of the given quantity of starch up to erythrodextrine under certain conditions. Wolgemut’s method can be used to approximately identify the activity of α–amylase in pancreatic juice, blood, urine and other biological liquids.
Put 1 ml of saliva into a test tube; add 9 ml of distilled water and mix. You get saliva solution 1:10.
Pour 1 ml of water into 10 enumerated test tubes. Add 1 ml of 10 times dissolved saliva to the first test tube by three times breathing in and out the liquid from the pipette. Then replace 1 ml of the liquid from the first test tube into the second one, mix the contents as it is mentioned before. Replace 1 ml of the liquid from the second test tube into the third one and so on.
Remove 1 ml of the liquid from the tenth test tube after mixing it.
Add 2 ml of 0,1% starch solution to all the test tubes beginning with the tenth one and mix the contents.
Place the test tubes into the thermostat at a temperature of 37°С for 30 minutes.
In 30 minutes cool the test tubes and add 1 drop of iodine solution in potassium iodide to all the test tubes. Mark the test tube where splitting of starch up to erythrodextrine has taken place and the latter gives red-brown coloring in reaction with iodine. The activity of α-amylase is expressed by the quantity of milliliters of 0,1% starch solution which can be split by 1 ml of undiluted saliva at a temperature of 37°С up to the stage of erythrodextrine during 30 minutes.
For example: if you observe red-brown coloring in the fourth test tube where the saliva is 160 times dissolved, it means that 1 ml of undiluted saliva would split 160 times more starch solution. Therefore, 1 ml of undiluted saliva splits during 30 minutes at 37°С: 2×160 = 320 ml of 0,1% starch solution. Symbolically these are 320 units of α-amylase according to Wolgemut:
А 37°/30' = 320 un.
Test questions
1. What are activators and inhibitors of enzymes?
2. How can the influence of activators and inhibitors upon the work of enzymes be investigated?
3. The enzyme acetylcholinesterase catalyses the hydrolysis of acetylcholine. It is neuromediator produced in the synapses of cholinergic nerves. Its breakdown products - acetate and choline – are unable to work as neuromediators. The hydrolysis of acetylcholine is stopped by calimine – a medicinal preparation used to heal motor disturbance after injuries, paralysis, in rehabilitating periods after having poliomyelitis, encephalitis, etc. The following scheme reflects the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase:
Inhibitor calimine
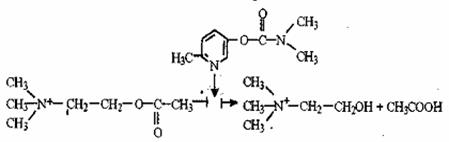
acetylcholine choline acetic acid
Compare the structural formulas of the inhibitor and the substrate. Why can one suppose that the inhibitor is bounding in the active centre of the enzyme? How will the influence of calimine change the conduction of nerve impulse (increase, reduce or will not change)?
Дата добавления: 2018-09-24; просмотров: 535;
