The influence of activators and inhibitors on the enzymes.
Activators of enzymes are ions of many metals. For example, calcium ions activate lipase. Some anions are also able to activate enzymes, for example α-amylase of saliva is activated by chloride ions.
Activators of enzymes can be a variety of agents, thus, bile acids increase the activity of pancreatic lipase.
Inhibitors inhibit enzymes action. Inhibitors are divided into reversible and irreversible. The basis of this division is the strength of the bond between inhibitor and enzyme.
Reversible inhibitors are compounds which form weak bonds with the enzyme and can be separated from the enzyme.
Reversible inhibition can be competitive. Competitive inhibitor has a structure similar to the structure of the substrate. It competes with substrate for binding at the active site. Competitive inhibition can be reduced or eliminated by increasing the concentration of the substrate. Competitive inhibitor increases Km, but does not alter Vmax.
Example: enzyme succinate dehydrogenase dehydrogenates succinate, converting it into fumarate. Malonate, which is structurally similar to succinate, binds to the active site of the enzyme, but cannot be dehydrogenated.
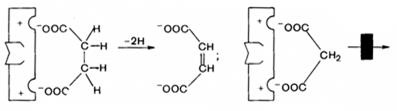
The degree of inhibition will be determined by the ratio of the concentrations of malonate and succinate.
Competitive inhibition method is widely used in medical practice. Sulfonamides are drugs used to treat infectious diseases. They are structural analogues of para-aminobenzoic acid, which participate in bacteria metabolism. Sulfonamide replaces para-aminobenzoic acid in the complex with the enzyme and it lead to the death of microorganisms.
Non-competitive inhibition is when a inhibitor does not compete with substrate for the enzyme active site. Substrate and inhibitor bind to different centers. Increasing the substrate concentration does not prevent the binding of the inhibitor. Noncompetitive inhibitor reduces the Vmax, while Km is not changed.
Un-competitive inhibition is known when the inhibitor binds to the enzyme in non-catalytic center, but not with the free enzyme, but only with the ES-complex. Un-competitive inhibitor decreases Vmax and increases Km.
Any agents that cause denaturation of proteins lead to irreversible inactivation of the enzyme. But it is not connected with the mechanism of enzyme action.
Irreversible inhibitors are compounds that can specifically bind to functionally important groups of the active center and form strong covalent bonds with the enzyme.
Non-competitive irreversible inhibition is caused by heavy metals (mercury, lead and others). They bind the HS-groups of the polypeptide chain. Salts of hydrocyanic acid, carbon monoxide (II) bind to the iron-containing prosthetic groups.
In competitive irreversible inhibition inhibitor has structural similarity with the substrate. It combines with the enzyme and replaces substrate.
Diisopropyl fluorophosphate is structurally similar to acetylcholine and can bind the enzyme acetylcholine esterase. It blocks the active site of the enzyme. As a result of the ability of neurons to conduct nerve impulses is lost.
The therapeutic effect of aspirin as an antipyretic and anti-inflammatory agent due to the fact that aspirin inhibits enzyme prostaglandin synthetase that catalyzes the synthesis of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are substances that participate in the development of inflammation. Inhibition is caused by acetylation of the amino group of the enzyme.
Дата добавления: 2018-09-24; просмотров: 1045;
