The calculation of the travel distance and angle between waypoints.
Currently used mainly two tracks: orthodromy and rhumb line.
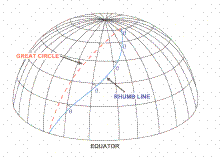
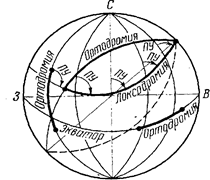
Depending on the type of course the instrument by which the course is maintained aircraft for a flight on the desired course, distinguish loxodromic and great circle piloting ways .
Loxodromic way - is realized by maintaining the course with the help of magnetic exchange instruments. For example, KI -13 , HIK -1 , TCS (KS) in the "MK". Great circle - when used for the purpose of exchange rate gyroscopic instruments. For example, HPK- 52, TCS (KS ) in the " Code of Civil Procedure ."
Thus, depending on the compass to withstand the rate path is a Loxodromic line or Orthodromy.
Orthodromy is called the arc of a great circle is the line of intersection of the surface of the sphere (approximating the Earth's surface) plane passing through its center . which is the shortest distance between two points on the surface of the globe. Orthodromy crosses the meridian at different angles.
The angle at which orthodromy a starting point ( plot) crosses the meridian is called the Orthodrome track angle OPU .
Special cases are the great circle meridians and the equator , when the income statement is constant and equal to the first case, 0 ° or 180 °, and in the second 90 ° or 270 °.
In other cases orthodromy crosses the meridian at different angles.
Calculation orthodromy direction (ie, track angle ) at the initial point according to the formula :
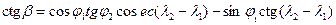 ,
,
where 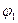 ,
, 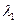 - the coordinates of the point where the track angle is calculated
- the coordinates of the point where the track angle is calculated
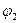 ,
, 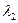 - - the coordinates of the second point of great circle .
- - the coordinates of the second point of great circle .
The calculation of the length of Orthodromy Sort results by value of deploying b performed using the formula:
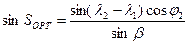
The calculation of the length of Great Circle between two points on a sphere is given by:
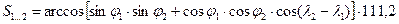
For a closer approximation to the radius of the chosen field (ie, increase the accuracy of the calculation S) ratio to 111.2 instead use the following method:
Convert the derived S ° to radians
(SРАД = S°×0,01752).
SRAD multiply the value of the sphere radius RE, which in this calculation is chosen to approximate the physical surface of the Earth.
In the current flight and navigation system calculation b and S orthodromy between POINS is performed using the more accurate formulas surveying the selected reference ellipsoid.
Application ortodromii map for distances exceeding 1000-1200 km to produce an intermediate point, longitude (l) which is selected as a rule with intervals of 10-20°. j breadth of each intermediate point orthodromy calculated using the formula:
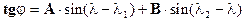 ,
,
where A and B - the factors constant for a given great circle, pre-calculated by the formulas:
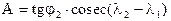 ,
,
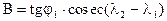 .
.
The calculated spherical latitude intermediate points should be converted into surveying, map and connect the smooth curve or line segments, which are the shortest distance between each start and end of POINT.
Loxodromic line is Line on the surface of the globe, crossing the meridian at a constant angle.
Given that the track angle (LSD) is constant on each meridian, and themselves meridians are not parallel to each other - loxodromic line is a logarithmic spiral that goes around the globe an infinite number of times and strive to the pole, but never reaches it. His bulge loxodrome is always facing toward the equator.
In general, the longer the great circle loxodromic line. Only in special cases when the flight is on the meridian or the equator, the length of the path loxodromic line and great circle will be the same. At large distances between destinations and flight, especially in the direction of the route, close to 90 ° or 270 °, the difference between the distances of the great circle and loxodrome reaches high values.
Loxodromic track angle (ZIPU) for each leg is measured directly on the map protractor regarding the central meridian of the site. And the length of the measured using a scale ruler. Or, more precisely, by the formulas of spherical trigonometry.
Track angle loxodrome to the coordinates of two of its points 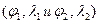 calculated by the formula:
calculated by the formula:
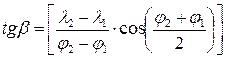 ,
,
where b - a sharp angle, -90 £ b <+90, and given the true track angle determined based on the direction of flight and is 360 ° + b or 180 ° + b.
Loxodrome length is determined by the formula:
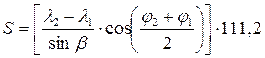 ,
,
where 111.2 - conversion factor angle values S in km (111,2 » 1,852×60).
Loxodrome length (in km) of travel angles close to 0 ° or 180 °, calculated as follows:
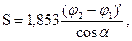
and for travel angles close to 90 ° or 270 °, the calculation is made as follows:
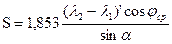
So, the loxodrome in all map projections, in which the meridians are not parallel lines, is a curve, but then when laying desired course between two points on the route (TM) uses the straight line. So the question - at what the limiting distance between the points deviation loxodrome will not exceed the tolerance of the center line of the route? To address this issue, we use the equation of the maximum lateral deviation from the loxodrome line connecting two points.
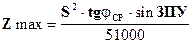
where S - distance desired course between two points,
j - average spherical latitude.
Zmax to replace the Zcounts and S to SLIMIT then
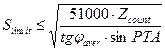
For example, it is necessary to determine the allowable distance between the TM in which the flight loxodromic method of piloting will not lead to a deviation from the axis of the route on Zcount = 1km, javer = 50°, and PTA = 90 °.
Decision.
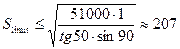 km
km
Conclusion: When a route for loxodromic way of piloting at a given latitude distance between points should not exceed 200 km.
THE POSITION LINE
Line of equal bearing
The line of equal distances
The Position line is the locus of points of the probable location of the plane corresponding to a constant value of the measured parameter navigation. In their navigation, the following main lines of position: great circle bearing line, the line is equal azimuths (radio bearing), the line of equal distances, and the line equal the difference of distances (hyperbole)..
Line of equal azimuth (line of equal radio bearing) line, for each point of radio navigation point) bearings under the same true bearing radio. Line of equal azimuth as the state line is used for the measurement of bearing radio stations using radio compass.The line of equal distances - a line all points of which are equidistant from a fixed point . On the surface of the globe equidistant line is a circle of a small circle . As the state line equidistant line is used when measuring distance using rangefinder and azimuth - range-finding systems.
Equal line for the distance - a line for each point . Difference of the distances to two fixed points on the earth's surface ( radio stations) is constant.
Дата добавления: 2015-06-10; просмотров: 4220;
