DIGITAL COMPUTER OPERATION
1. A digital computer is a machine capable of performing operations on data represented in digital or number form. The individual operations performed by a digital computer are very simple arithmetic or logical processes involving the manipulation of the bits in words or characters of information. The great power of any digital computer rests in the ability to store large volumes of data and to perform these operations at extremely high speed.
In most electronic digital computers the method of number representation is based on the system of binary notation. The binary notation system is most widely used because of the convenience in constructing logical circuits and storage devices capable of handling data in this form. For example, a magnetic memory unit consists of many thousand individual magnetic cells, each of which can be energized in either of two ways to represent the binary digits 0 or 1. If these cells are grouped to form words or binary coded characters, information can be
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 94
 stored for processing in units of specified size. In the same way, digital data can be recorded as a series of magnetized spots on a magnetic tape or a magnetic disk.
stored for processing in units of specified size. In the same way, digital data can be recorded as a series of magnetized spots on a magnetic tape or a magnetic disk.
2. The computer has pervaded most fields of human activity and is the most important innovation of our age. Born out of the technology of communication, it is capable of handling enormous amounts of information at tremendous speeds. What makes it so potent is the fact that a single mechanism can perform any information-processing task. The same mechanism can control industrial processes, guide space vehicles or help to teach children. This diversity of tasks is made possible by the simple idea of the stored program.
A program is the enumeration of determining commands. It specifies the method used for the solution of a problem in detail. When the machine is. in operation, both the commands and the numbers to be processed are constantly being taken out of and put into a depository of information known as a memory.
It can be seen that the processes performed by a digital computer are essentially simple. These operations can be performed at extremely high speeds and with a high degree of coordination between the different functional units of the hardware system, and this ability means that digital computers can undertake highly complex tasks.
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
It is well known in computer science that the words 'computer' and 'processor' are used interchangeably. Speaking more precisely, 'computer* refers to the central processing unit (CPU) together with an internal memory. The internal memory, control and processing components make up the heart of the computer system. Manufactures design the CPU to control and carry out basic instructions for their particular computer.
The CPU coordinates all the activities of the various components of the computer. It determines which operations should be carried out and in what order. The CPU controls the operation of the entire system by issueing commands to other parts of the system and by acting on responses. When required it reads information from the memory, interprets instructions, performs operations on the data according to the instructions, writes the results back into the memory and moves information between memory levels or through the input-output ports.
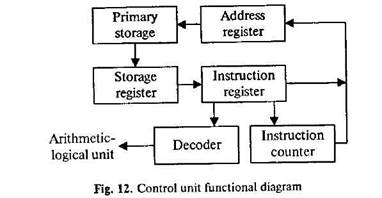
In4igital computers the CPU can be divided into two functional units called the control unit (CU) and the arithmetic-logical unit (ALU). These two units are made up of electronic circuits with millions of switches that can be in one of two states, either on or off.
The function of the CU within the central processor is to transmit coordinating control signals and commands. The control unit is that part of the computer that directs the sequence of step-by-step operations of the system, selects instructions and data from memory, interprets the program instructions, and controls the flow between main storage and the arithmetic-logical unit.
The ALU, on the other hand, is that part of the computer in which the actual arithmetic operations, namely, addition, subtraction* multiplication, division and exponentiation, called for in the instructions are performed.
|
| Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 100 |
Programs and the data on which the CU and the ALU operate, must be in internal memory in order to be processed. Thus, if located in secondary memory devices, such as disks or tapes, programs and data are first loaded into internal memory.
Дата добавления: 2015-06-05; просмотров: 2254;
