Three important concepts in encryption.
Private and public keys. One of the most important concepts in the encryption - key. The common encryption schemes have a private key that is kept secret on your computer and allows you to read messages addressed to you. Since you can also put the private key to send messages is protected against forgery digital signature. The public key - the file that you can share with others or publish. It allows people to share with you encrypted messages and to verify your signature. Private and public key - pair. They are like two halves of a stone, two exactly suited to each other, but dissimilar parts.
Safety Certifications. Another very important concept - a security certificate. The web browser on your computer can establish an encrypted connection with websites via HTTPS. In such cases, the browser verifies the certificate by checking public keys of domain names (eg, www.google.com, www.amazon.com and ssd.eff.org). Using Certificates - one way to confirm the authenticity of your existing public key person or a website, so you can securely exchange information with him.
The network from time to time you will see a message about a security certificate error. As a rule, the reason is to try the hotel or an Internet cafe, where you are, "open" your encrypted data exchange with the website. In addition, this error often occurs because of bureaucratic problems in the certificate system. But sometimes it occurs when you try to hacker thief, police authority or the security services to crack your encrypted connection.
Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult to establish the true cause. Therefore, when a security certificate error can not take exception to websites where you have an account or where you get very important information.
Prints keys.
The word "print" in the field of computer security can mean many different things. One of the options - "print key": a sequence of characters, such as 342e 2309 bd20 0912 ff10 6c63 2192 1928. The print key allows you to securely authenticate the private key used by anyone on the Internet. If the test print is passed, more likely that the other person is really who he claims to be. This method is not perfect: the attacker can use the same print, copy.
Questions:
1. What are the threats to information security and their classification?
2. What is cyber security industry?
3. What are there measures and the protection of the media?
4. Standards and information security specifications.
5. When is founded a law on information security?
6. What is a Digital Signature?
References
1. June J. Parsons and Dan Oja, New Perspectives on Computer Concepts 16th Edition - Comprehensive, Thomson Course Technology, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc Cambridge, MA, COPYRIGHT © 2014.
2. Lorenzo Cantoni (University of Lugano, Switzerland) James A. Danowski (University of Illinois at Chicago, IL, USA) Communication and Technology, 576 pages.
3. Craig Van Slyke Information Communication Technologies: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications (6 Volumes). ISBN13: 9781599049496, 2008, Pages: 4288
4. Utelbaeva A.K.,Utelbaeva A.K. Study guide for lectures on discipline “Computer science”, Shimkent 2008, 84 pages.
Lecture №9 Internet technologies.
Purpose: іntroduce Internet to the student, to provide an introduction to the e-mail.
Plan:
1. Basic concepts Internet. The universal identifier of resources (URI), its assignment and components.Service DNS.
2. Web technologies: HTTP, DHTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
3. E-mail. Message format.
4. SMTP, POP3, IMAP protocols.
1. Basic concepts Internet. The universal identifier of resources (URI), its assignment and components.Service DNS.
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a form of URI and is a standardized naming convention for addressing documents accessible over the Internet and Intranet. An example of a URL is http://www.computerhope.com, which is the URL for the Computer Hope website.
Overview of a URL
Below is additional information about each of the sections of the http URL for this page.

http://
The "http" stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol and is what enables the browser to know what protocol it is going to use to access the information specified in the domain. After the http is the colon( : ) and two forward slashes ( //) that separate the protocol from the remainder of the URL.
www.
Next, www.stands for World Wide Web and is used to distinguish the content. This portion of the URL is not required and many times can be left out. For example, typing "http://computerhope.com" would still get you to the Computer Hope web page. This portion of the address can also be substituted for an important sub page known as a subdomain. For example, http://support.computerhope.com forwards you to the main help section of Computer Hope.
computerhope.com
Next, computerhope.com is the domain name for the website. The last portion of the domain is known as the "domain suffix", or TLD, and is used to identify the type or location of the website. There are dozens of other domain suffixes available. To get a domain, you would register the name through a domain registrar.
/jargon/u/
Next, the "jargon" and "u" portions of the above URL are the directories of where on the server the web page is located. In this example, the web page is two directories deep, so if you were trying to find the file on the server, it would be in the /public_html/jargon/u directory. With most servers, the public_html directory is the default directory containing the HTML files.
url.htm
Finally, url.htm is the actual web page on the domain you're viewing. The trailing .htm is the file extension of the web page that indicates the file is an HTML file. Other common file extensions on the Internet include .html, .php, .asp, .cgi, .xml, .jpg, and .gif. Each of these file extensions performs a different function, just like all the different types of files on your computer.
The structure of the URL is shown in the figure below.
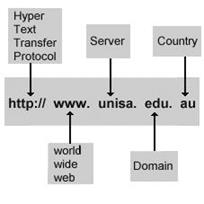
Figure 22: Structure of the URL
There are several domains available in the web such as:
edu = education institute
com = commercial enterprise
gov = government
org = organization
net = network provider
mil = military
2. Web technologies: HTTP, DHTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Internet Protocols
| Internet | Refersto | Description | Internet |
| Protocol | Services | ||
| SMTP | SimpleMailTransfer | A protocol for sending e- | |
| Protocol | mail messages between | ||
| servers | |||
| POP3 | PostOfficeProtocol | Used by local e-mail clients to | |
| version 3 | retrieve e-mail from a remote | ||
| server over a TCP/IP | |||
| connection | |||
| FTP | FileTransferProtocol | This is used to transfer files | Transferring |
| from one host to another host | files | ||
| over a TCP-based network, | |||
| suchastheInternet. | |||
| HTTP | HyperTextTransfer | Define show messages are | WorldWide |
| Protocol | formatted and transmitted, | Web(www) | |
| and what actions Web | |||
| server sand browsers should | |||
| take in response to the wide | |||
| range of commands. | |||
| HTTPS | HyperTextTransfer | Provides authentication of | WorldWide |
| ProtocolSecure | the web site and associated | Web(www) | |
| web server andprotects | |||
| against man-in-the-middle | |||
| attacks. | |||
| VoIP | VoiceoverInternet | This enables people to use | Online |
| Protocol | the Internet as the | chat(thereare | |
| transmission medium for | exceptions) | ||
| telephone calls. | |||
Table 10- The Internet Protocols
The Internet uses a variety of languages to transmit information from one place to the other. These languages are called protocols. Using these protocols we can acquire the services from the Internet. Each protocol has a specific functionality and www is considered to be the largest service acquired amongst the services provided by the Internet.
Internet is an interconnection of computer networks all around the world. In other words, it is the hardware which forms the physical layer to these connections is what we refer to as the Internet. Hence, the Internet comprises of network of computers, fiber-optic cables, copper wires and wireless networks. But www is the software which is used to access the information from the Internet. It consists of files, folders and the documents which are stored in different computers. Now it is crystal clear to you that the www depends on the Internet to work.
Дата добавления: 2017-05-18; просмотров: 1700;
