A polymer of nucleotides
 Each DNA strand is a polymer made up of nucleotide subunits. Тhe nucleotides join together to form long unbranched polynucleotide chains.
Each DNA strand is a polymer made up of nucleotide subunits. Тhe nucleotides join together to form long unbranched polynucleotide chains.
Each nucleotide consists of deoxyribose (a five-carbon or pentose sugar), an organic nitrogen-containing base (of which there are four different types), and phosphoric acid.
The sugar and the organic base join together by a condensation reactionto form a nucleoside. (A condensation reaction results in the removal of a water molecule.)
Another condensation reaction joins the nucleoside with phosphoric acid to form the nucleotide. This bond forms between carbon 5 of the sugar and the phosphate, and is called a phosphoester bond.
The organic bases present in DNA are either purines (guanine, G and adenine, A) or pyrimidines (cytosine, С and thymine, T). Purines have a double ring structure; pyrimidines have a single ring structure.
Two nucleotides can join together by a condensation reaction between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group on carbon 3 of the sugar of the other nucleotide. The bonds linking the nucleotides together are strong, covalent phosphodiesterbonds.
The process can be repeated so that a polynucleotide chain builds up. The chain has a sugar-phosphate backbone with the organic bases projecting outwards.
Each chain has two distinct ends: a 3' ('three prime') end and a 5'('five prime') end. At the 3' end, the carbon 3 of the deoxyribose is closest to the end; at the 5' end, the carbon 5 of the deoxyribose is closest to the end.
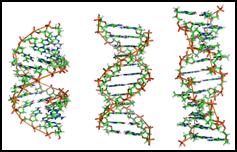
 The double helix
The double helix
DNA consists of two polynudeotide chains coiled around each other to form a double helix. The double helix is held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases in the two chains. The pairings depend on the shapes of the bases (a purine can only bond with a pyrimidine) and on their ability to form hydrogen bonds:
Adenine (a purine) pairs with thymine (a pyrimidine), forming two hydrogen bonds (A=T).
 Guanine (a purine) pairs with cytosine (a pyrimidine), forming three hydrogen bonds (G = C).
Guanine (a purine) pairs with cytosine (a pyrimidine), forming three hydrogen bonds (G = C).
Дата добавления: 2015-11-04; просмотров: 1048;
