Composition Nanoparticles
Pure metal Au, Ag, Pd, Pt, Cu, Co, Ni, Ru, etc
Bimetal Fe-Co, Co-Ni, Pd-Au, etc.
Alloy FePt, CoPt, PdNi, PtRu, etc.
Semiconductor GaAs, CdTe, CdSe, CdS, ZnSe, AgBr, etc.
Oxide SiO2, Al2O3, TiO2, CeO2, Fe3O4, ZrO2 , ZnO, SnO2 2, etc.
A variety of different shapes of nanoparticles have been identified. This includes sphere, prism, cube, tetrapod, branched, triangle, hexagon, and pentagon.

sphere prism cube tetrapod
Their shapes can also be tube, rod, needle, and hollow sphere.

Tube rod needle hollow sphere
Carbon nanotubes and peptide nanotubes are typical examples of the tube-type of nanoparticles. Fullerene-based particles and a variety of organic, inorganic, polymeric, or biological nanosized capsules (such as vesicles) can be classified as typical hollow sphere types. To build fullerenes spheroids are necessary combinations of pentagons and hexagons. If we ignore the pentagons, stable molecules are also obtained in the form of hollow cylinders called carbon nanotubes. Later we will study these kind nanomaterials.
Nanoparticles, also can be classified taking into account their geometric form and dimension of the structural elements of which they are constituted: 0D-(Zero-dimensional) clusters; 1D-(One-dimensional) nanotubes, fibers and rods; 2D-(Two-dimensional) films and coats; 3D-(Three-dimensional) polycrystals
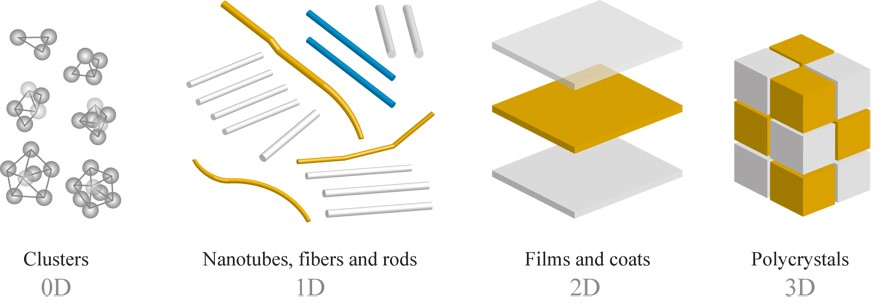
1. Zero dimensional(0-D): These nanomaterials have Nano-dimensions in all the three directions. Metallic nanoparticles including gold and silver nanoparticles and semiconductor such as quantum dots are the perfect example of this kind of nanoparticles. Most of these nanoparticles are spherical in size and the diameter of these particles will be in the 1-50 nm range. Cubes and polygons shapes are also found for this kind of nanomaterials.
2. One dimensional(1-D): In these nanostructures, one dimension of the nanostructure will be outside the nanometer range. These materials are long (several micrometers in length), but with diameter of only a few nanometer. Nanowire and nanotubes of metals, oxides and other materials are few examples of this kind of materials
3. Two dimensional(2-D): In this type of nanomaterials, two dimensions are outside the nanometer range. These include different kind of Nano films such as coatings and thin-film-multilayers, nano sheets or nano-walls. The area of the nano films can be large (several square micrometer), but the thickness is always in nano scale range
4. Three Dimensional(3-D): All dimensions of these are outside the nano meter range. These include bulk materials composed of the individual blocks which are in the nanometer scale (1-100 nm)
We already know that nanomaterials are a collective term that combines the extensive substance classes, sizes of the structural elements which lie within the range of 1 to 100 nm.
Дата добавления: 2018-11-25; просмотров: 595;
