Synthesis of glucose from the pyruvic acid.
The first step is the formation of phosphoenolpyruvate from pyruvic acid.
a)Carboxylation of pyruvic acid under the influence of pyruvate carboxylase leads to the formation of oxaloacetate in mitochondria:
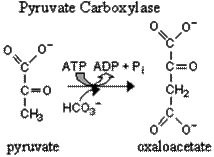
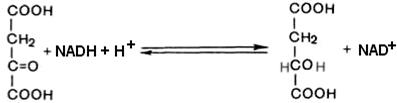
Pyruvate carboxylase is mitochondrial biotin-dependent enzyme, allosteric activator of which is acetyl-KoA. Mitochondrial membrane is impermeable for oxaloacetate, so oxaloacetate in the mitochondria is converted to malate with the participation of mitochondrial NAD-dependent malate dehydrogenase:
|
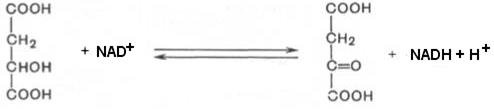
Malate leaves the mitochondria through the mitochondrial membrane into the cytosol, where it is oxidized to oxaloacetate under the action of the cytoplasmic NAD-dependent malate dehydrogenase:
|
b) in the cell cytosol decarboxylation and phosphorylation of oxaloacetate are proceeded to form phosphoenolpyruvate. The enzyme catalyzing this reaction is phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase:
|
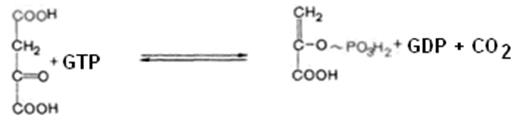
CO2 is liberated. GTP is used in this reaction. So, on this stage 2 ATP equivalents are used. Then PEP undergoes the reversal of glycolysis until fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is produced.
The second stage is the conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into fructose-6-phosphate.
Phosphoenolpyruvate as a result of reversible reactions of glycolysis is converted to fructose-1,6-phosphate. Then an irreversible phosphofructokinase reaction of glycolysis is followed. Gluconeogenesis is bypassing this reaction:
|
 Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + H2O Fructose-6-phosphate
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + H2O Fructose-6-phosphate
+ Pi
This enzyme required Mg2+ ions.
The third stage is the formation of glucose from fructose-6-phosphate.
Fructose-6-phosphate is converted to glucose-6-phosphate, which is dephosphorylated under the influence of glucose-6-phosphatase:
|
 Glucose-6-phosphate + H2O Glucose + Pi
Glucose-6-phosphate + H2O Glucose + Pi
Reaction is bypasses hexokinase reaction.
Enzymes of three irreversible stages of gluconeogenesis are regulatory enzymes.
The overall summary of gluconeogenesis is:
2 pyruvate + 2 NADH + 4 ATP + 2 GTP ® glucose + 2 NAD+ + 4 ADP +
+ 2 GDP + 6 Pi
Дата добавления: 2018-09-24; просмотров: 364;
