Proteins containing non-heme iron.
Ferritin (about 20% iron) is concentrated mainly in splean, liver and bone marrow. It plays the role of iron storage in the body.
Serum transferrin (about 0.13% iron) transports iron ions in reticulocytes, which made the biosynthesis of hemoglobin.
2. Metalloenzymes are proteins that have enzymatic activity and containing metal cations. In metalloenzymes protein bond with the metal more stable. Enzymes that are activated by metal ions are less strongly associated with metals.
ATPase contains Na, K, Ca, Mg, alcohol dehydrogenase - Zn, cytochrome oxidase - Cu, proteinase - Mg, K.
6. Nucleoproteins(NP) are stable complexes of nucleic acids and proteins.
NUCLEIC ACIDS
Nucleic acids – RNA and DNA – are polymers of nucleotides.
DNA is found in the cell nucleus and mitochondria.
RNA is found in all parts of the cell. We distinguish messenger RNA (mRNA). It synthesized by DNA and determines the order of amino acids in a protein molecule. Ribosomal RNA (r-RNA) is part of the ribosome. Transport RNA (t-RNA) carries amino acids to the place of protein synthesis.
NA provide storage and transmission of genetic information by programming the synthesis of cellular proteins.
Bases of NA – DNA: purine - A, G, pyrimidine – C, T; RNA: purine – A, G, pyrimidine – C, U. One of the important properties of free nitrogenous bases is that they can exist in two tautomeric forms. Also NA containe carbohydrates (ribose and deoxyribose) and phosphoric acid residues.
Nucleotides consist of three components: a pyrimidine or purine base, a pentose and phosphoric acid (fig. 7). Nucleotides are nucleoside phosphates.
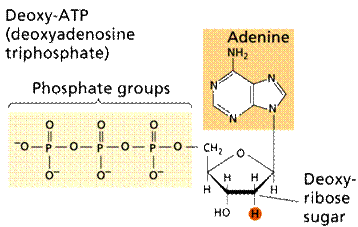
|
| Fig. 7. Nucleotide structure |
To study the chemical composition of NA using sequencing - splitting up into fragments by enzymes or chemical reagents. Products are analyzed by electrophoresis, chromatography, etc.
DNA isolated from different tissues of the same species, has the same composition of the nitrogenous bases. Analysis of DNA composition and the quantity of bases was established for the first time by Erwin Chargaff, Austrian-born American biochemist. The quantitative relations were named Chargaff's rules.
1. The quantity of purine bases (in moles) is equal to the quantity of pyrimidine bases: A + G = C + T.
2. The quantity of adenine and cytosine is equal to the quantity of guanine and thymine: A + C = G + T.
3. The quantity of adenine is always approximately equal to that of thymine, and the quantity of guanine is always approximately equal to that of cytosine.
A = T, G = C.
4. The A/G ratio varies widely from species to species. The coefficient of specificity is (G + C) / (A + T) (0,54 - 0,94 in animals, 0,45-2,57 in microorganisms).
Дата добавления: 2018-09-24; просмотров: 455;
