The structure of the national economy.
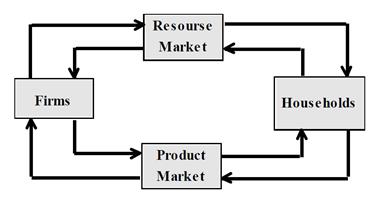
Macroeconomic analysis is based on a simple circular flow model(GNP, income and expenditures circular flow model). Its easiest form contains only two types of economic agents - households and firms, and supposes no government interference, as well as no transactions with the rest of the world.
Firms' expenditure on resources (or their costs) present at the same time flows households' incomes, such as labor income, rent and others. On the other hand, consumer expenditure flows form sales revenue (or income) of firms producing goods and services.
"Income-expenditure" and "resources-products" flows are realized simultaneously and are resumed endlessly. Total value of sales in the model necessarily equals total amount of households' incomes. Therefore, total value of output in a closed economy(i.e. that with no relations with the rest of the world) and with no government interference equals total value of households' income.
Value of output characterize results of economic activity on the macro-level. It can be estimated either on national or on domestic base. To explain the difference between these two methods we introduce the concepts of resident and non-resident sectors.
Resident sectorincludes all the citizens of a country living in its territory or abroad or receiving compensation from the budget of the country. Non-resident sectorincludes all the people, either citizens or not, living and promoting economic activity in the territory of the country. It means, that economic activities of other countries citizens are to be taken into consideration here, but activities of the given country citizens excluded.
Accordingly, there are two main macroeconomic indicators - Gross Domestic Product (GDP)and Gross National Product (GNP).
GDPmeasures the value of goods and services produced in the territory of a country, i.e. by the factors of production of a given economy, regardless of their owner. It includes the results of non-resident sector economic agents economic activities.
GNPmeasures the results of economic activity on the national basis, so it includes the value of all goods and services produced by the resident sector factors of production, i.e. owned by its citizens. Some share of GNP is produced abroad.
The difference between GDP and GNP equals the difference between resident and nonresident factor incomes. GNP = GDP + net factor income from abroad.
The method of final utilizationpresents market value of all consumed by the economic agents goods and services. It is the sum of expenditures of households, firms, government and foreigners exporting from the country.
GDP = C + I + G + Xn , where:
C- personal consumption expenditures, including those on durable goods, nondurable goods and on services and excluding dwelling expenditures;
I- investment expenditures. Only private investment expenditures are taken into consideration here, and government investments are accounted separately.
G- government consumption: government expenditures on goods (purchased by government) and services (compensation of government officials and financing public sector institutions). Government transfers do not contribute to the increase of output, and so they are not included here.
Xn- net exports - the difference between export and import values.
Дата добавления: 2015-10-05; просмотров: 1623;
