Law of supply and the supply curve. Non-price factors influencing to changes in supply. Factors affecting supply.
Supply (S): A relationship between price and the quantity sellers are willing and able to sell.
Quantity supplied (QS ):The amount of an item that would be supplied at a certain price given all of the other influences on supply.
The supply of commodity QS depends not only on the commodity's price P, but on many other factors (Non-price determinants):
- the technology used (T): the rise of technology level shifts supply curve outward, because producer can propose higher quantity of commodity produced under the same price but lower costs;
- the inputs' prices (Pi ): the rise of an input price shifts the supply curve inward, because producer can propose lower quantity of commodity produced under the same price but higher costs);
- expectations of future changes in price (E),
- number of sellers (only for market supply): the growth of producers number shifts the supply curve outward if producers do not diminish their supply when new producers occur;
- market organization (taxes and subsidies): the growth of taxes level decreases a good's supply and thus shifts commodity's supply curve inward, the subsidies move it outward;
- special influences.
The Law of Supply says that as the price P goes up, the quantity supplied QS also goes up, ceteris paribus (i.e. if the other factors considered above are constant).
Supply curve:A graph of the relationship between price and quantity supplied (Fig.2.5). The positive (upward) slope of the supply curve reflects the law of supply.
Let's consider a following scale of the offer (tab. 2.2)
| The price for 1 writing-book (P), tenge | Size of the offer of writing-books a week (QS), pieces |
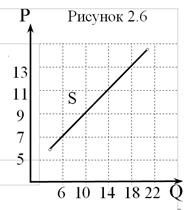
Moving along the supply curve S is called change in quantity supplied (Fig.2.6). Change in quantity supply:A change in the amount of an item offered for sale in response to a change in its price, other things being equal. In this situation a change in price p is accompanied in general by a change in quantity q.
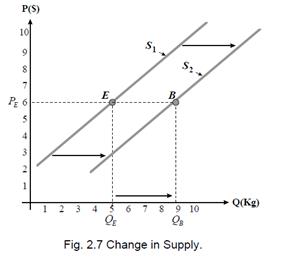
A shift of supply curve (it may be not a parallel shift) is called a change of supply (Fig.2.7). Change in supply: A change in the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied that results from a change in something other than the price of the good (non-price determinants changes).
Дата добавления: 2015-10-05; просмотров: 1610;
