Meiosis: four different daughter cells
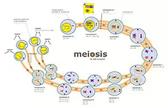 In meiosis, the nucleus divides twice. This produces four haploid nuclei. The number of chromosomes is therefore halved during meiosis. Moreover, homologous chromosomes within a pair can exchange genetic material before being separated. The daughter cells are therefore genetically different from the parent cell (and from each other).
In meiosis, the nucleus divides twice. This produces four haploid nuclei. The number of chromosomes is therefore halved during meiosis. Moreover, homologous chromosomes within a pair can exchange genetic material before being separated. The daughter cells are therefore genetically different from the parent cell (and from each other).
Meiosis is the basis of sexual reproduction, occurring at some point in the life cycle of organisms that reproduce sexually. The haploid gametes produced by meiosis fuse during fertilization. This means that the new fertilized cell has the diploid number of chromosomes. Without meiosis in the life cycle, the number of chromosomes of a sexually reproducing species would be doubled in each generation.
Дата добавления: 2015-07-06; просмотров: 952;
