Important Points To Note For Maintenance Of Emergency Generators On Ship
Any kind of emergency equipment or system provided onboard is an important lifeline for the ship and its crew when faced with an emergency situation. Emergency Generator is without doubt one of the most important equipment on board, which is responsible for preventing accidents and grounding during power failure while the ship is in heavy traffic, channels, rough weather or in manoeuvring.
The Emergency Generator on ship comes into play as back up source of power when the main generators fails to provide the necessary power to the engine room and other deck machinery systems.
Considering its high importance, the emergency generator is required to be tested regularly along with carrying out all important planned maintenance jobs as per schedule. This would not only ensure smooth running of the emergency generator but would also avoid breakdown when the ship is already facing a distress situation.
Following are some important maintenance jobs that need to be carried out in emergency generators on ships:
1. Change of Engine Sump Oil: It is important to check the oil level in the sump regularly. Since the emergency generator is kept on auto mode, which ensures the generator starts and comes on load automatically, it is necessary that before starting the engine for operation, oil level is checked on regularly basis. The condition of the oil will be known during this period and if the oil is having carbon or soot particles, change of complete oil system needs to be done. The running hours for changing of engine oil depends on the manufacturer, the engine make and the oil grade in use. Normally it is done between 250-500 hrs.
The oil changing period must be cut by half when the fuel used in generator is more than 0.5% to 1% sulfur.
2. Clean Air Cleaner: The combustion air for the engine is passed through an air filter, which can be of following types:
1. oil bath air cleaner
2. dry type air cleaner (cartridge or dust collector).
It is important to clean the air filter at correct intervals of time as delay will lead to clogging and less air going in the engine. This will reduce the efficiency of the engine and increase the thermal parameters. When using dry cartridge, ensure to replace them at intervals stated by the maker. Normal replacement schedule is one year or after 5-7 cleanings.
3. Check Water Separator: Some emergency generators are provided with water separator to prevent mixing of water with fuel. Check the level of water and make sure it is below the marked level and regularly drained off. This is to be done to avoid rust and corrosion of fuel line devices and to avoid incomplete combustion.
4. Check Electrolyte in the Battery: A battery is used in one of the starting methods of the emergency generator. The electrolyte level in the battery must be checked at regular intervals either by inserting a level stick or by checking the water level in the level tester cap (if provided). Use distilled water to make up for the low level.
5. Check Alarms and Shutdowns: All the safety devices and alarms fitted in the emergency generator must be checked and tested regularly. Generator with V-belts have additional alarm which will be sounded in the event of belt failure and operated by idler pulley.
6. Check V belt Tension: When V belt is fitted, inspect the same for cracks and damages. Renew the belt if damage/ cracking appearance is more. To check the belt tension, press the belt by thumb in midway of the pulleys and check the inward deflection in mm. It should not be more than 10-15 mm depending upon the make of the generator.
7. Clean Oil Filter Cartridge: The emergency generator is provided with various oil filters such as by pass filter, centrifuge filter, lube oil filter, fuel feed pump filter etc. These filters need to be cleaned or renewal of filter cartridge is to be carried out as per the maker’s instruction or oil condition.
8. Check Valve Clearance: The tappet clearance of the inlet and exhaust valve should be checked at running hours stated in the maintenance section of the generator’s manual. Also ensure the engine is cold before taking the tappet clearance.
Loss of emergency generators at times when they are needed the most can lead to unfortunate and disastrous incidents. Followed a proper planned maintenance system along with thorough regular checks is the key to ensure smooth running of emergency generators on board ships.
Important Things To Check In Ship’s Engine Bedplate
A bedplate is the lowermost portion of a marine engine (2 and 4 stroke), which supports the engine structure and is also one of the most loaded constructional parts of the engine. For large engines, the bedplate is fabricated in parts with flat bottom type construction having high surface finish. The bedplate is later arranged together during installation in large engines, whereas for smaller engines the bedplate is fully casted. For large bedplates the material used can be cast or prefabricated steel or a mixture of both. The important requirement for large engine bedplate is to use material with low carbon steel with maximum carbon content of 0.23%. For small bedplate, cast iron with internal vibration damping characteristics is used, which reduces the frequency of cracks in the bedplate. The main components of any bedplate are longitudinal and cross girders.
The important functions of bedplate are:
- To support the static load of stationary engine frame and blocks
- To support the dynamic load of the running gear
- To support the crankshaft and hold it in perfect alignment
- To distribute the static and dynamic load generated by running engine onto the ship structure
- To collect the crankcase lube oil and transfer it to the sump tank from where the lube oil pump can take suction
- To fasten the engine to the tank top transmitting propeller thrust to the hull structure
- To contribute to the hull strength of the ship at engine room bottom structure
It is important to keep a regular check on the bedplate as it’s the foundation of the marine engine. The inspection of bedplate is also included in the planned management system of engine.
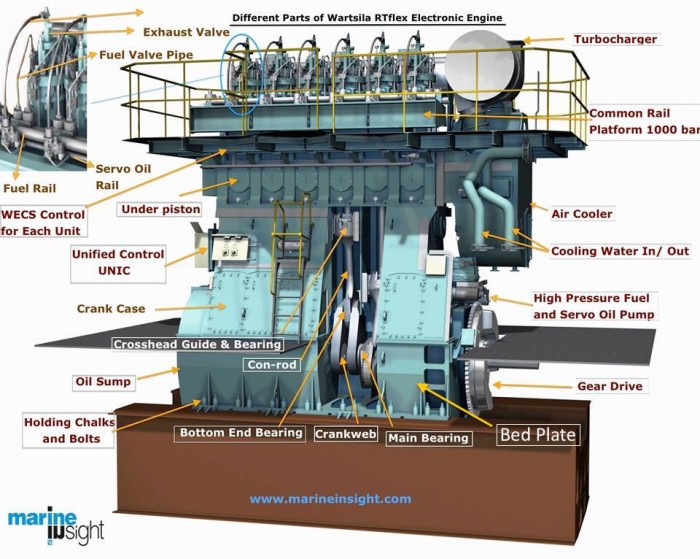
Following checks to be carried on the bedplate during inspection:
Cracks: Cracks is the most common problem that occurs on the bedplate structure. Following areas to be carefully checked for cracks:
- Welding portion which joins the transverse girders to the longitudinal girders
- Under the bearing pockets where cracks can emerge to be radial or follow the line of the pocket which holds the bearing
- Radially at tie bolt and frame bolt holes
- Around lightening holes provided in the bedplates and girders
- At the base of main bearing keeps
Faulty welding: It is to be checked on newly delivered engine or if any welding repairs are carried out in the recent past
Faulty casting – It is to be checked on newly delivered engine with casting construction
Corrosion: As the bedplate is the bottom structure fitted in the bilge section of the engine room, it comes in contact with various fluids such as oil, water etc. and therefore is prone to corrosion. A close check should be made for identifying corrosion.
Loose Frames: The bedplate is held together with A frame and entablature of the engine by means of tie rod. Check the tie rod is tightened and there is no loose portion between the frame and bedplate.
Faulty Holding Down Bolts: The holding down bolts keeps the bedplate in position with the bottom structure of the ship. Check for loose holding down bolts and tighten as per the manual if found loose. Also, check for shearing and fretting on the holding down bolts.
Oil leakages: The bedplate is also responsible to collect the lube oil and transfer it to engine sump. Check for any oil leakage from the bedplate or the joint between the bedplate and the frame.
Ship’s engineers are responsible to ensure that marine engine bedplate is inspected at regular intervals of time and all faults are identified and repaired at the earliest. Failing to do so will result in heavy vibrations, misalignment of crankshaft, and reduction in engine efficiency and failure of engine components.
20 Possible Causes for Reduction in Ship’s Auxiliary Engine Performance
Power generation is a continuous requirement on board ships. A blackout situation even for few minutes can lead to devastating results such as grounding, collision etc., resulting in heavy losses and danger to the ship and its crew.
A ship is equipped with multiple generators/ auxiliary engines to supply continuous power at all times. These power generating units are watched over and maintained by ship engineers.
A sensible ship engineer will try to run minimum number of generators at any given period of time and look for maximum load, which not only ensures goodwill for the auxiliary engines but also reduces overall fuel consumption and harmful emissions. This can happen when the auxiliary engine rated output is achieved without any deviation in the engine parameters (temperature, pressure etc.).
If the engine performance is deteriorating, it will result in reduced output with high exhaust temperature and low peak pressure. The reduced output of one generator will require another generator to run in parallel and compensate the power demand.
Ship engineers must know the probable reasons which can lead to reduced power output of auxiliary engines.
Following are 20 possible causes, which will lead to reduced power output and performance of an auxiliary engine on board ship:
1. Fuel oil pressure too low: The fuel oil pressure is lower than requirement, which can be due to faulty fuel oil attached pump or the fuel oil viscosity is very low
2. Type of Fuel Burned: The fuel oil pressure will also drop when the fuel grade is changed from HFO to MDO/ MGO/LSFO. This will lead to decrease in engine performance
3. Fuel leakage: If the fuel pump parts i.e plunger and barrels are worn out, the fuel will leak out and the fuel pressure will drop at the discharge point
4. Fuel Temperature: If the fuel temperature is inadmissibly high (>60 deg C), the fuel viscosity will reduce and it will affect the fuel pressure
5. Firing Pressure Difference: If there is high difference firing pressure in between individual cylinders, it will lead to reduction in overall output of the engine
6. Blocked Filter: Blocked or dirty line filters in the fuel oil system will reduce the oil pressure and hence the performance
7. Wrong Valve Clearance: The clearance between intake/ exhaust valve and its guides is of extreme importance. If the clearance is more than required, the combustion mixture will leak out from this gap and reduce the engine performance
8. Damaged Exhaust Valve: A damaged exhaust valve or seat will not seal properly causing blow-by of exhaust gasses on combustion. This will increase the exhaust temperature and reduce engine output
9. High Exhaust Back Pressure: If there is a flaw in the exhaust piping installation or the silencer is fouled, it will lead to high exhaust gas pressure and increase in exhaust temperature of all units
10. Contaminated Passages: A contaminated exhaust manifold will lead to hindrance in the exhaust gas flow and increase the exhaust temperature
Дата добавления: 2016-05-16; просмотров: 2181;
