Cell membrane
The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, encloses the cell. It is made up of lipid, protein and a small amount of carbohydrate. The functions of the cell membrane are:
1.Protection of the cytoplasm and its organelles.
2.Exchange of material into or out of the cell.
3.Provides the cell with shape.
4.Links cells to each other and provides communication between cells.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the second main part of the cell. The cytoplasm is located .between the cell membrane and the nucleus. It is jelly-like (like egg white) in structure. It contains organic and inorganic materials.
Cell organelles are found in the cytoplasm. Cell organelles are the micro- organs of the cell. They have special functions in the cell. We can summarize their function as follows.
1.Ribosomes produce protein.
2.Mitochondria are the power houses of the cell. They produce ATP energy.
3.Golgi bodies are the packaging system of the cell. They produce special materials such as milk.
Vacuoles are the storage centers of the cell. They store water, minerals and waste.
Lysosomes are the stomach of the cell. They enable digestion in the cell.
Peroxisomes are the disposal centers of the cell. They destroy harmful substances.
Endoplasmic reticulum is the transport system of the cell. It produces proteins, lipids and other substances and transports them through the cytoplasm.
Chloroplasts are found in plant cells. They produce food and oxygen by photosynthesis.
Centrosomes are found in animal cells. They aid in cell division.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell (you could say the brain of the cell). In the nucleus, genetic material (chromosomes, made up of DNA and protein) is found. The nucleus also contains the nucleolus, which produces ribosomes.
Other structures of the eukaryotic cell
Cell wall: It is a hard structure which protects the cell. For example, plant cells have a rigid structure because of the cell wall.
Flagellum and cilia: They enable movement of the cell. A flagellum is long, but cilia are short.
Material transport through the cell membrane
The cell membrane has a selectively permeable structure. That means it allows some materials to pass into or out of the cytoplasm. Some materials can pass, but others cannot pass through the cell membrane. Materials exchange is provided for by different methods, including diffusion, osmosis and active transport.

Diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. For example, perfume diffuses throughout г room until its concentration is constant. The cell doe: not use energy for this process, so it can occur in living and non-living cells.
Osmosis
Osmosis is the diffusion of water. Water molecule: move from where they are highly concentrated to where there is a low concentration. Like diffusion energy is not used and osmosis occurs in living and nonliving cells.
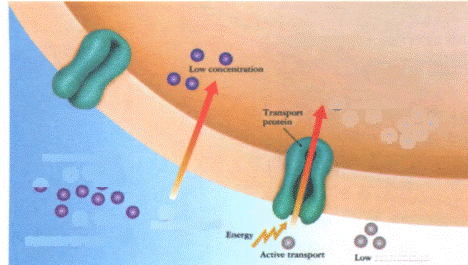
Active transport
Active transport is the movement of molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration. In this process cells use energy. Unlike diffusion and osmosis, it occurs only in living cells.
 |
KARTINKA RAKA
Дата добавления: 2015-02-05; просмотров: 950;
