The Internet 1: email and newsgroups
When different networks are connected together, the combined network is called an internetwork or internet. The connection of networks throughout the world forms what is known as the Internet. Networks all over the world are connected to the Internet using electronic devices known as routers. The routers decide which rout on the Internet a particular signal should take to get to its destination. Users often pay a monthly fee to a type of company known as an Internet service provider (ISP), to provide them with an Internet connection. A variety of services such as email and file transfer are made available to users on the Internet. These services are controlled using a system of server computers at various locations throughout the world.
Electronic mail, which has come to be known as email, is one of the most popular services on the Internet. Email allows users to send electronic messages to storage areas known as mailboxes on server computers where they can be read by other users. Each user has their own email address which determines where their email messages are stored. Every email address has two main parts separated by an at symbol, i.e. username@ domain name. The domain name may be subdivided using dots. A typical email address might have the following components:
Username @ server . type of . country
or identifier name organization
Standard codes are used for the types of organization, although they may vary slightly from country to country. Not all email addresses use all the possible parts of the domain name. An email message has two main parts known as the header and the body of the message. The body contains the message itself, whilst the header reveals the identity of the recipient and of the sender, the date it was sent, and the subject title of the message. The most basic type of email consists of plain text to which other types of computer files, such as formatted text, spreadsheets, sound files, or video files can be attached. These email attachments can then be opened and read using an appropriate program on the recipient’s computer.
Groups of users that share a special interest can subscribe to free newsgroups on the Internet. Subscribers can send plain text messages to a common area on a server computer where all the newsgroup members can read them. In this way, conversations about the special interest can take place between all the members of the group. The name of the newsgroup is made up of different parts separated by dots and indicates the specialist area the subscribers are interested in. For example, newsgroup names that begin with alt indicate that they deal with alternative types of subjects, e.g. alt.tasteless-jokes. Newsgroup names beginning with rec deal with recreational subjects, e.g. rec.chess. When you are replaying to a message, it is common for the email program to include the original message with each line marked with a chevron (>), and if you are replaying to a reply, each line of the original text is marked with double chevrons (>>). In this way the correspondents can keep track of the conversation.
13 The Internet 1:
email and newsgroups
Tuning-in
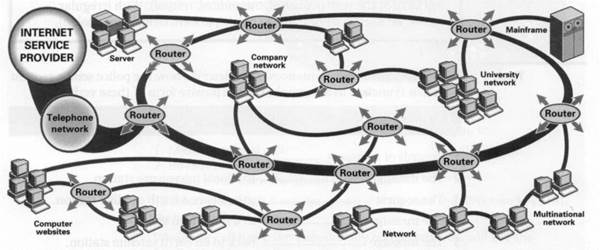
Task 1 Study this diagram of the Internet. With its help, match these definitions to the correct item on the diagram.
1 a device which selects the best route to send data from one network to another
2 a specialist computer which provides a service to a network
3 a company which provides Internet access
4 a large multi-user computer for processing very large amounts of data
5 computers connected together to share hardware and software
Task 2 Do you use the Internet? What do people use the Internet for? Make a list and discuss it with your group.
Listening: Email
Task 3 Study this email. Answer these questions.
1 Who is the sender? 4 What is it about?
2 What is his email address? 5 What time was the message sent?
3 Who is it sent to? 6 In what form is the main part of the message?

Task 4 Now listen to the attachment and find the answers to these questions.
1 When did he start his course?
2 Why is Friday different from other days?
3 Which class does he most enjoy?
4 What is he thinking of for a project?
5 Why does he not like the maths lecturer?
6 What sport does he play at lunch-time?
7 What's happening on the 17th?
8 Where will it be?
9 Who will be there?
Reading: Newsgroups
Task 5 You can exchange views on almost any subject by joining an Internet
newsgroup. Which of these groups would interest the following people (1-6)?
a alt.algebra.help f alt.sport.soccer.european
b alt.asian-movies g alt.tasteless-jokes
с alt.comics.batman h rec.antiques.bottles
d alt.education.disabled i alt.food.wine
e alt.fashion j alt.music.world
1 a football fan 4 a comic book collector
2 a student with maths problems 5 a fan of Indian cinema
3 a bottle collector 6 someone interested in clothes
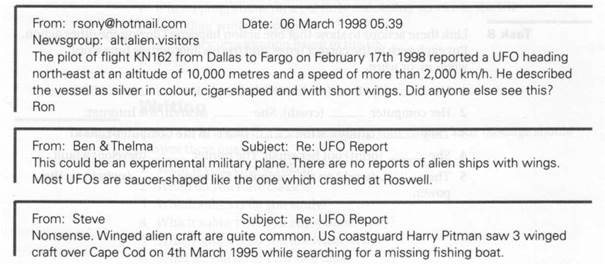
Task 6 Study this exchange between subscribers to a newsgroup and find the answers to these questions.
1 What newsgroup is this? 6 Who sent the second message?
2 Who sent the first message? 7 What was the object?
3 When did he send it? 8 Why do they think so?
4 Where was flight KN162 going? 9 What did the coastguard see?
5 What did the pilot see? 10 What was he doing?
| Language work: Past simple vs Past continuous |
| We make the Past continuous with was/were + the -ing form of the verb. We often use it to provide the context for actions in the past. |
| He was flying from Dallas to Fargo. He saw a UFO. (action 1) (action 2) |
| To show that one past action happened in the middle of another past action, we can link them using when, as, and while. He was flying from Dallas to Fargo when he saw a UFO. As he was flying from Dallas to Fargo, he saw a UFO. While he was flying from Dallas to Fargo, he saw a UFO. |
| We use the Past simple for completed actions, especially those which take very little time. We use the Past continuous to describe actions which happen over a period of time. He saw a UFO. It was heading north-east. It was travelling at 2,000 km/h. |
Task 7 Put the verb in brackets into the Past simple or the Past continuous.
1 The plane ______________ (go) to Fargo.
2 The UFO _________________ (fly) at 10,000 metres.
3 The pilot _____________ (notice) it had short wings.
4 The pilot ______________ (report) the incident.
5 He _______________ (describe) the vessel as silver in colour.
6 No one else __________ (see) the UFO.
7 The UFO __________ (head) north-east.
8 The coastguard ___________ (see) three winged craft.
9 He __________ (search) for a missing fishing boat.
10 A UFO ____________ (crash) at Roswell.
Task 8 Link these actions to show that one action happened during the other action. Put each verb in the correct tense, and use an appropriate time word: while, as, or when.
1 He _________ (fly) from London to Edinburgh. He _________ (see) a UFO.
2 Her computer _______ (crash). She ___________ (search) the Internet.
3 They _________ (study). A fire __________ (start) in the Computer Lab.
4 She ____________ (print) out her email. The printer __________ (develop) a fault.
5 They _____________ (work) on the computer. Someone ___________ (switch) on the
power.
Problem-solving
Study this typical email address. It belongs to Anna Lock, who works for the Pesto company in the UK.
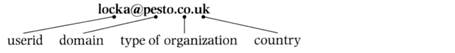
Study these examples of types of organizations and countries.
| <== предыдущая лекция | | | следующая лекция ==> |
| Computing Support Assistant | | | The Internet 2: the World Wide Web |
Дата добавления: 2016-04-26; просмотров: 4863;
